Ralstonia paucula (Formerly CDC group IV c-2): unsuccessful strain differentiation with PCR-based methods, study of the 16S-23S spacer of the rRNA operon, and comparison with other Ralstonia species (R. eutropha, R. pickettii, R. gilardii, and R. solanacearum)
- PMID: 11136807
- PMCID: PMC87738
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.1.381-384.2001
Ralstonia paucula (Formerly CDC group IV c-2): unsuccessful strain differentiation with PCR-based methods, study of the 16S-23S spacer of the rRNA operon, and comparison with other Ralstonia species (R. eutropha, R. pickettii, R. gilardii, and R. solanacearum)
Abstract
Ralstonia paucula (formerly CDC group IV c-2) can cause serious human infections. Confronted in 1995 with five cases of nosocomial bacteremia, we found that pulsed-field gel electrophoresis could not distinguish between the isolates and that randomly amplified polymorphic DNA analysis was poorly discriminatory. In this study, we used PCR-ribotyping and PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the spacer 16S-23S ribosomal DNA (rDNA); both methods were unable to differentiate R. paucula isolates. Eighteen strains belonging to other Ralstonia species (one R. eutropha strain, six R. pickettii strains, three R. solanacearum strains, and eight R. gilardii strains) were also tested by PCR-ribotyping, which failed to distinguish between the four species. The 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer of R. paucula contains the tRNA(Ile) and tRNA(Ala) genes, which are identical to genes described for R. pickettii and R. solanacearum.
Figures
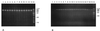
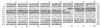
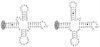
References
-
- Aspinall S T, Graham R. Two sources of contamination of a hydrotherapy pool by environmental organisms. J Hosp Infect. 1989;14:285–292. - PubMed
-
- Bidet P, Barbut F, Lalande V, Burghoffer B, Petit J C. Development of a new PCR-ribotyping method for Clostridium difficile based on ribosomal RNA gene sequencing. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999;175:261–266. - PubMed
-
- Coenye T, Falsen E, Vancanneyt M, Hoste B, Govan J R W, Kersters K, Vandamme P. Classification of Alcaligenes faecalis-like isolates from the environment and human clinical samples as Ralstonia gilardii sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1999;49:405–413. - PubMed
-
- Forman W, Axelrod P, St John K, Kostman J, Khater C, Woodwell J, Vitagliano R, Truant A, Satishchandran A, Fekete T. Investigation of a pseudo-outbreak of orthopedic infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1994;15:652–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

