Hyper-immunoglobulin A in the hyperimmunoglobulinemia D syndrome
- PMID: 11139196
- PMCID: PMC96011
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.8.1.58-61.2001
Hyper-immunoglobulin A in the hyperimmunoglobulinemia D syndrome
Abstract
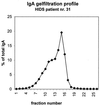
The hyperimmunoglobulinemia D syndrome (HIDS) is an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by recurrent febrile attacks with abdominal, articular, and skin manifestations. Apart from elevated immunoglobulin D (IgD) levels (>100 IU/ml), there are high IgA levels in the majority of cases. Mutations in the gene encoding mevalonate kinase constitute the molecular defect in HIDS. The cause of elevated IgA concentrations in HIDS patients remains to be elucidated. We studied the hyper-IgA response in serum of a group of HIDS patients. Elevated IgA concentrations result from increased IgA1 concentrations. IgA and IgA1 concentrations correlated significantly with IgD concentrations, and levels of IgA polymers were significantly higher than the levels in healthy donors. These results indicate a continuous, presumably systemic, stimulation of IgA in HIDS patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of inflammatory attacks in the classical type hyper-IgD syndrome on immunoglobulin D, cholesterol and parameters of the acute phase response.J Intern Med. 2004 Sep;256(3):247-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2004.01359.x. J Intern Med. 2004. PMID: 15324368
-
Hyperimmunoglobulinemia D and periodic fever syndrome (HIDS) in a child with normal serum IgD, but increased serum IgA concentration.J Pediatr. 2003 Jul;143(1):127-9. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(03)00212-9. J Pediatr. 2003. PMID: 12915839
-
Favorable preliminary experience with etanercept in two patients with the hyperimmunoglobulinemia D and periodic fever syndrome.Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Sep;48(9):2645-51. doi: 10.1002/art.11218. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. PMID: 13130485
-
[Identification of the gene for hyper-IgD syndrome: a model of modern genetics].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2000 Apr 22;144(17):782-5. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2000. PMID: 10800545 Review. Dutch.
-
Mevalonate kinase deficiencies: from mevalonic aciduria to hyperimmunoglobulinemia D syndrome.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2006 Apr 26;1:13. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-1-13. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2006. PMID: 16722536 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mevalonate kinase deficiency: an updated clinical overview and revision of the SHARE recommendations.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 12;15:1466844. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1466844. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39600705 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic causes of high and low serum HDL-cholesterol.J Lipid Res. 2010 Aug;51(8):2032-57. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R004739. Epub 2010 Apr 26. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 20421590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Establishment of a transgenic mouse model with liver-specific expression of secretory immunoglobulin D.Sci China Life Sci. 2012 Mar;55(3):219-27. doi: 10.1007/s11427-012-4301-3. Epub 2012 Apr 14. Sci China Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22527518 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulin class-switch recombination: Mechanism, regulation, and related diseases.MedComm (2020). 2024 Aug 13;5(8):e662. doi: 10.1002/mco2.662. eCollection 2024 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39144468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deletion of a single mevalonate kinase (Mvk) allele yields a murine model of hyper-IgD syndrome.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2007 Nov;30(6):888-95. doi: 10.1007/s10545-007-0776-7. Epub 2007 Nov 19. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2007. PMID: 18008182
References
-
- Boom B W, Daha M R, Vermeer B J, van der Meer J W M. IgD immune complex vasculitis in a patient with hyperimmunoglobulinemia D and periodic fever. Arch Dermatol. 1990;126:1621–1624. - PubMed
-
- Conley M E, Delacroix D L. Systemic immunization can result in polymeric IgA production. Pediatr Res. 1986;20:293A.
-
- Conley M E, Delacroix D L. Intravascular and mucosal immunoglobulin A: two separated but related systems of immune defense? Ann Intern Med. 1987;106:892–899. - PubMed
-
- Cooper E H, Turner R, Johns E A, Crockson R A. Identification and measurement of paraprotein polymers by high performance gel filtration chromatography. Biomed Pharmacother. 1985;39:78–82. - PubMed
-
- Delacroix D L, Liroux E, Vaerman J P. High proportion of polymeric IgA in young infants' sera and independence between IgA size and IgA subclass distributions. J Clin Immunol. 1983;3:51–56. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous