Seroepidemiology of human group C rotavirus in Japan based on a blocking enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- PMID: 11139211
- PMCID: PMC96026
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.8.1.161-165.2001
Seroepidemiology of human group C rotavirus in Japan based on a blocking enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
Abstract
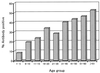
A novel blocking enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (BL-ELISA) was developed for detection of antibodies to human group C rotavirus (CHRV). The specificity of the BL-ELISA was confirmed by using animal sera hyperimmunized to group A and group C rotaviruses and paired sera from five patients with acute CHRV gastroenteritis. Furthermore, there was concordance between the BL-ELISA and a neutralization assay for CHRV in 226 (95%) of 238 samples. By using the BL-ELISA, we determined the seroprevalence of CHRV in 704 serum samples obtained from nine different age groups of inhabitants of Okayama Prefecture, Japan, in 1992, 1994, and 1996. As a result, 211 sera (30%) were found to be positive for CHRV antibodies. The seroprevalence gradually increased with age and reached 52.7% in the oldest individuals. A further analysis of the youngest age group suggested that CHRVs predominantly prevail in persons older than 3 years of age in Japan. When comparing the three sampling years, a larger percentage of antibody-positive sera was detected in 1994 than in either 1992 or 1996 in individuals between 6 and 15 years of age, reflecting the occurrence of a CHRV outbreak among children during the winter of 1992 to 1993 that was previously documented. These results indicate that CHRV infections may occur more frequently in spite of the relatively low detection rate of the virus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection and molecular characterization of human group C rotaviruses in Okayama Prefecture, Japan, between 1986 and 2005.J Med Virol. 2007 Aug;79(8):1219-28. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20910. J Med Virol. 2007. PMID: 17596825
-
Detection of antibody to group B adult diarrhea rotaviruses in humans.J Clin Microbiol. 1987 May;25(5):812-8. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.5.812-818.1987. J Clin Microbiol. 1987. PMID: 3034964 Free PMC article.
-
Neutralization assay for human group C rotaviruses using a reverse passive hemagglutination test for endpoint determination.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Jan;38(1):50-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.1.50-54.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10618062 Free PMC article.
-
[Outbreak of acute gastroenteritis caused by human group C rotavirus in a youth educational center in Okayama Prefecture].Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 2003 Feb;77(2):53-9. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.77.53. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 2003. PMID: 12661079 Japanese.
-
Detection of group C rotavirus antigens and antibodies in animals and humans by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays.J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Aug;30(8):2129-34. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.8.2129-2134.1992. J Clin Microbiol. 1992. PMID: 1323577 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Seroepidemiology of group C rotavirus infection in England and Wales.Eur J Epidemiol. 2004;19(6):589-95. doi: 10.1023/b:ejep.0000032381.36658.cb. Eur J Epidemiol. 2004. PMID: 15330133
-
Rotavirus Infection in Children Suffering from Diarrhea in Patna, Bihar Region, India: A Hospital-Based Study.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2025 Feb 25;112(5):1040-1043. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.24-0543. Print 2025 May 7. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2025. PMID: 39999449
-
Molecular characterization of a human group C rotavirus detected first in Turkey.Virus Genes. 2009 Oct;39(2):157. doi: 10.1007/s11262-009-0420-8. Epub 2009 Nov 15. Virus Genes. 2009. PMID: 19916043
-
Detection and quantification of group C rotaviruses in communal sewage.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008 Jun;74(11):3394-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02895-07. Epub 2008 Apr 4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18390677 Free PMC article.
-
Seroepidemiology of Human Non-Species A Rotavirus Infections in Valencia, Spain.J Med Virol. 2025 Aug;97(8):e70542. doi: 10.1002/jmv.70542. J Med Virol. 2025. PMID: 40751697 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bass D M, Greenberg H B. Group A rotaviruses. In: Blaser M J, Smith P D, Ravdin J I, Greenberg H B, Guerrant R L, editors. Infections of the gastrointestinal tract. New York, N.Y: Raven Press, Ltd.; 1995. pp. 967–982.
-
- Bonsdorf C H V, Svensson L. Human serogroup C rotavirus in Finland. Scand J Infect Dis. 1988;20:475–478. - PubMed
-
- Caul E O, Ashley C R, Darville J M, Bridger J C. Group C rotavirus associated with fatal enteritis in a family outbreak. J Med Virol. 1990;30:201–205. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials