Highly conserved features of DNA binding between two divergent members of the Myb family of transcription factors
- PMID: 11139623
- PMCID: PMC29659
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.2.527
Highly conserved features of DNA binding between two divergent members of the Myb family of transcription factors
Abstract
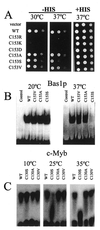
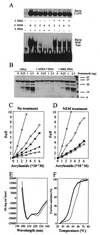
Bas1p, a divergent yeast member of the Myb family of transcription factors, shares with the proteins of this family a highly conserved cysteine residue proposed to play a role in redox regulation. Substitutions of this residue in Bas1p (C153) allowed us to establish that, despite its very high conservation, it is not strictly required for Bas1p function: its substitution with a small hydrophobic residue led to a fully functional protein in vitro and in vivo. C153 was accessible to an alkylating agent in the free protein but was protected by prior exposure to DNA. The reactivity of cysteines in the first and third repeats was much lower than in the second repeat, suggesting a more accessible conformation of repeat 2. Proteolysis protection, fluorescence quenching and circular dichroism experiments further indicated that DNA binding induces structural changes making Bas1p less accessible to modifying agents. Altogether, our results strongly suggest that the second repeat of the DNA-binding domain of Bas1p behaves similarly to its Myb counterpart, i.e. a DNA-induced conformational change in the second repeat leads to formation of a full helix-turn-helix-related motif with the cysteine packed in the hydrophobic core of the repeat.
Figures
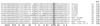



References
-
- Ness S.A. (1996) The Myb oncoprotein: regulating a regulator. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1288, 123–139. - PubMed
-
- Oh I.H. and Reddy,E.P. (1999) The myb gene family in cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis. Oncogene, 18, 3017–3033. - PubMed
-
- Frampton J., Gibson,T.J., Ness,S.A., Doderlein,G. and Graf,T. (1991) Proposed structure for the DNA-binding domain of the Myb oncoprotein based on model building and mutational analysis. Protein Eng., 4, 891–901. - PubMed
-
- Gabrielsen O.S., Sentenac,A. and Fromageot,P. (1991) Specific DNA binding by c-Myb: evidence for a double helix-turn-helix-related motif. Science, 253, 1140–1143. - PubMed
-
- Ogata K., Morikawa,S., Nakamura,H., Sekikawa,A., Inoue,T., Kanai,H., Sarai,A., Ishii,S. and Nishimura,Y. (1994) Solution structure of a specific DNA complex of the Myb DNA-binding domain with cooperative recognition helices. Cell, 79, 639–648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

