In situ detection of hepatitis C virus RNA in salivary glands
- PMID: 11141499
- PMCID: PMC1850261
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63964-8
In situ detection of hepatitis C virus RNA in salivary glands
Abstract
Chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection has been associated with several extrahepatic manifestations, among these, to diseases with oral manifestations such as Sjögren's syndrome or sialadenitis. HCV-RNA has been detected in saliva and in salivary glands from patients with sialadenitis by polymerase chain reaction. However, morphological evidence of HCV replication in salivary gland cells is needed to support a role for HCV in causing sialadenitis or Sjögren's syndrome. We have used in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry to analyze the presence of HCV-RNA of sense and antisense polarity and HCV core antigen, respectively, in salivary gland biopsies from 19 patients with chronic sialadenitis or Sjögren's syndrome (eight anti-HCV-positive; 11 anti-HCV-negative). HCV-RNA of both positive and negative polarity as well as HCV core antigen were detected in the epithelial cells of the salivary gland biopsies from all of the anti-HCV-positive patients but in none of the anti-HCV-negative cases. The percentage of HCV-infected cells ranged from 25 to 48.8% in the patients studied. In conclusion, we have shown that HCV infects and replicates in the epithelial cells from salivary glands of patients with Sjögren's syndrome or chronic sialadenitis. However, its implication in the pathogenesis of these diseases deserves future research.
Figures
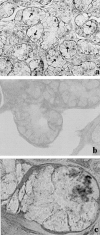
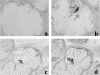
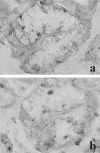

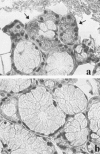
Comment in
-
Is hepatitis C virus a sialotropic virus?Am J Pathol. 2001 Oct;159(4):1593-4. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62543-6. Am J Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11583984 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kuo G, Choo QL, Alter HJ, Gitnick GL, Redeker AG, Purcell RM, Miyamura T, Dienstag JL, Alter MJ, Stevens CE, Tegtmeier GE, Bonino F, Colombo M, Lee WS, Kuo C, Berger K, Shuster JR, Overby LR, Bradley DW, Houghton M: An assay for circulating antibodies to a major etiologic virus of human non-A, non-B, hepatitis. Science 1989, 244:362-364 - PubMed
-
- Robertson B, Myers G, Howard C, Brettin T, Bukh J, Gaschen B, Gojobori T, Maertens G, Mizokami M, Nainan O, Netesov S, Nishioka K, Shini T, Simmonds P, Smith D, Stuyver L, Weiner A: Classification, nomenclature, and data base development for hepatitis C virus (HCV) and related viruses: proposal for standardization. Arch Virol 1998, 143:2493-2503 - PubMed
-
- Clarke B: Molecular virology of hepatitis C virus. J Gen Virol 1997, 78:2397-2410 - PubMed
-
- Di Bisceglie AM: Hepatitis C. Lancet 1998, 351:351-355 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

