Maturation of steroid receptors: an example of functional cooperation among molecular chaperones and their associated proteins
- PMID: 11147968
- PMCID: PMC312893
- DOI: 10.1379/1466-1268(2000)005<0076:mosrae>2.0.co;2
Maturation of steroid receptors: an example of functional cooperation among molecular chaperones and their associated proteins
Abstract
The selective modulation of transcription exerted by steroids depends upon recognition of signalling molecules by properly folded cytoplasmic receptors and their subsequent translocation into the nucleus. These events require a sequential and dynamic series of protein-protein interactions in order to fashion receptors that bind stably to steroids. Central to receptor maturation, therefore, are several molecular chaperones and their accessory proteins; Hsp70, Hsp40, and hip modulate the 3-dimensional conformation of steroid receptors, permitting reaction via hop with Hsp90, arguably the central protein in the process. Binding to Hsp90 leads to dissociation of some proteins from the receptor complex while others are recruited. Notably, p23 stabilizes receptors in a steroid binding state, and the immunophilins, principally CyP40 and Hsp56, arrive late in receptor complex assembly. In this review, the functions of molecular chaperones during steroid receptor maturation are explored, leading to a general mechanistic model indicative of chaperone cooperation in protein folding.
Figures

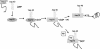

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
