Emergence of diverse Helicobacter species in the pathogenesis of gastric and enterohepatic diseases
- PMID: 11148003
- PMCID: PMC88962
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.14.1.59-97.2001
Emergence of diverse Helicobacter species in the pathogenesis of gastric and enterohepatic diseases
Abstract
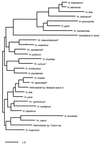
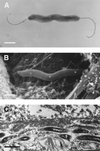
Since Helicobacter pylori was first cultivated from human gastric biopsy specimens in 1982, it has become apparent that many related species can often be found colonizing the mucosal surfaces of humans and other animals. These other Helicobacter species can be broadly grouped according to whether they colonize the gastric or enterohepatic niche. Gastric Helicobacter species are widely distributed in mammalian hosts and are often nearly universally prevalent. In many cases they cause an inflammatory response resembling that seen with H. pylori in humans. Although usually not pathogenic in their natural host, these organisms serve as models of human disease. Enterohepatic Helicobacter species are an equally diverse group of organisms that have been identified in the intestinal tract and the liver of humans, other mammals, and birds. In many cases they have been linked with inflammation or malignant transformation in immunocompetent hosts and with more severe clinical disease in immunocompromised humans and animals. The purpose of this review is to describe these other Helicobacter species, characterize their role in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal and enterohepatic disease, and discuss their implications for our understanding of H. pylori infection in humans.
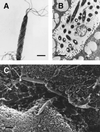
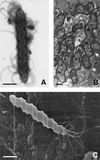
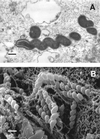
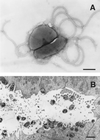
Figures

References
-
- Adam W S, Calhoun M L, Smith E M, Stinson A W. Microscopic anatomy of the dog. Springfield, Il: Charles C Thomas; 1970.
-
- Akin O Y, Tsou V M, Werner A L. Gastrospirillum hominis-associated chronic active gastritis. Pediatr Pathol Lab Med. 1995;15:429–435. - PubMed
-
- Alder J D, Ewing P J, Mitten M J, Oleksijew A, Tanaka S K. Relevance of the ferret model of Helicobacter-induced gastritis to evaluation of antibacterial therapies. Am J Gastroenterol. 1996;91:2347–2354. - PubMed
-
- al-Himyary A J, Zabaneh R I, Zabaneh S S, Barnett S. Gastrospirillum hominis in acute gastric erosion. South Med J. 1994;87:1147–1150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

