Nuclear localization of NPR1 is required for activation of PR gene expression
- PMID: 11148282
- PMCID: PMC102222
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.12.12.2339
Nuclear localization of NPR1 is required for activation of PR gene expression
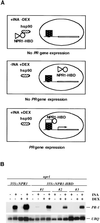
Abstract
Systemic acquired resistance (SAR) is a broad-spectrum resistance in plants that involves the upregulation of a battery of pathogenesis-related (PR) genes. NPR1 is a key regulator in the signal transduction pathway that leads to SAR. Mutations in NPR1 result in a failure to induce PR genes in systemic tissues and a heightened susceptibility to pathogen infection, whereas overexpression of the NPR1 protein leads to increased induction of the PR genes and enhanced disease resistance. We analyzed the subcellular localization of NPR1 to gain insight into the mechanism by which this protein regulates SAR. An NPR1-green fluorescent protein fusion protein, which functions the same as the endogenous NPR1 protein, was shown to accumulate in the nucleus in response to activators of SAR. To control the nuclear transport of NPR1, we made a fusion of NPR1 with the glucocorticoid receptor hormone binding domain. Using this steroid-inducible system, we clearly demonstrate that nuclear localization of NPR1 is essential for its activity in inducing PR genes.
Figures
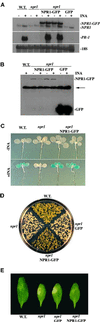
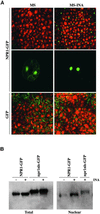
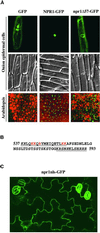
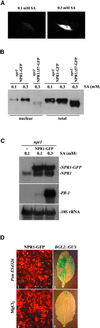
Similar articles
-
Identification and cloning of a negative regulator of systemic acquired resistance, SNI1, through a screen for suppressors of npr1-1.Cell. 1999 Aug 6;98(3):329-39. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81962-5. Cell. 1999. PMID: 10458608
-
Evidence for a disease-resistance pathway in rice similar to the NPR1-mediated signaling pathway in Arabidopsis.Plant J. 2001 Jul;27(2):101-13. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.2001.01070.x. Plant J. 2001. PMID: 11489188
-
The Arabidopsis NPR1/NIM1 protein enhances the DNA binding activity of a subgroup of the TGA family of bZIP transcription factors.Plant Cell. 2000 Feb;12(2):279-90. Plant Cell. 2000. PMID: 10662863 Free PMC article.
-
[Nonexpressor of pathogenesis-related genes 1 (NPR1): a key node of plant disease resistance signalling network].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2005 Jul;21(4):511-5. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2005. PMID: 16176083 Review. Chinese.
-
Systemic acquired resistance: turning local infection into global defense.Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2013;64:839-63. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-042811-105606. Epub 2013 Jan 25. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2013. PMID: 23373699 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrating data on the Arabidopsis NPR1/NPR3/NPR4 salicylic acid receptors; a differentiating argument.Front Plant Sci. 2015 Apr 10;6:235. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2015.00235. eCollection 2015. Front Plant Sci. 2015. PMID: 25914712 Free PMC article.
-
A rice transient assay system identifies a novel domain in NRR required for interaction with NH1/OsNPR1 and inhibition of NH1-mediated transcriptional activation.Plant Methods. 2012 Feb 21;8(1):6. doi: 10.1186/1746-4811-8-6. Plant Methods. 2012. PMID: 22353606 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis Rho of plants GTPase AtROP6 functions in developmental and pathogen response pathways.Plant Physiol. 2013 Mar;161(3):1172-88. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.213165. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Plant Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23319551 Free PMC article.
-
The Underexplored Mechanisms of Wheat Resistance to Leaf Rust.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 28;12(23):3996. doi: 10.3390/plants12233996. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38068630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elongator subunit 3 positively regulates plant immunity through its histone acetyltransferase and radical S-adenosylmethionine domains.BMC Plant Biol. 2013 Jul 16;13:102. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-13-102. BMC Plant Biol. 2013. PMID: 23856002 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander, D., Goodman, R.M., Gut-Rella, M., Glascock, C., Weymann, K., Friedrich, L., Maddox, D., Ahl-Goy, P., Luntz, T., Ward, E., and Ryals, J. (1993). Increased tolerance to two oomycete pathogens in transgenic tobacco expressing pathogenesis-related protein 1a. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90 7327–7331. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aoyama, T., and Chua, N.-H. (1997). A glucocorticoid-mediated transcriptional induction system in transgenic plants. Plant J. 11 605–612. - PubMed
-
- Aravind, L., and Koonin, E.V. (1999). Fold prediction and evolutionary analysis of the POZ domain: Structural and evolutionary relationship with the potassium channel tetramerization domain. J. Mol. Biol. 285 1353–1361. - PubMed
-
- Beato, M. (1989). Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell 56 335–344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

