Targeting Pyk2 to beta 1-integrin-containing focal contacts rescues fibronectin-stimulated signaling and haptotactic motility defects of focal adhesion kinase-null cells
- PMID: 11149924
- PMCID: PMC2193658
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.152.1.97
Targeting Pyk2 to beta 1-integrin-containing focal contacts rescues fibronectin-stimulated signaling and haptotactic motility defects of focal adhesion kinase-null cells
Abstract
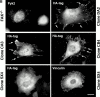
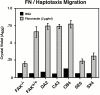
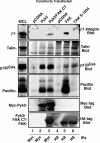
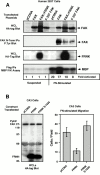
Focal adhesion kinase-null (FAK(-/-) fibroblasts exhibit morphological and motility defects that are reversed by focal adhesion kinase (FAK) reexpression. The FAK-related kinase, proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (Pyk2), is expressed in FAK(-/-) cells, yet it exhibits a perinuclear distribution and does not functionally substitute for FAK. Chimeric Pyk2/FAK proteins were created and expressed in FAK(-/-) cells to determine the impact of Pyk2 localization to focal contacts. Whereas an FAK/Pyk2 COOH-terminal (CT) domain chimera was perinuclear distributed, stable expression of a Pyk2 chimera with the FAK-CT domain (Pyk2/FAK-CT) localized to focal contact sites and enhanced fibronectin (FN)-stimulated haptotactic cell migration equal to FAK-reconstituted cells. Disruption of paxillin binding to the FAK-CT domain (S-1034) inhibited Pyk2/FAK-CT localization to focal contacts and its capacity to promote cell motility. Paxillin binding to the FAK-CT was necessary but not sufficient to mediate the indirect association of FAK or Pyk2/FAK-CT with a beta 1-integrin-containing complex. Both FAK and Pyk2/FAK-CT but not Pyk2/FAK-CT S-1034 reconstituted FAK(-/-) cells, exhibit elevated FN-stimulated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK2) and c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) kinase activation. FN-stimulated FAK or Pyk2/FAK-CT activation enhanced both the extent and duration of FN-stimulated ERK2 activity which was necessary for cell motility. Transient overexpression of the FAK-CT but not FAK-CT S-1034 domain inhibited both FN-stimulated ERK2 and JNK activation as well as FN-stimulated motility of Pyk2/FAK-CT reconstituted cells. These gain-of-function studies show that the NH(2)-terminal and kinase domains of Pyk2 can functionally substitute for FAK in promoting FN-stimulated signaling and motility events when localized to beta-integrin-containing focal contact sites via interactions mediated by the FAK-CT domain.
Figures







References
-
- Arthur W.T., Petch L.A., Burridge K. Integrin engagement suppresses RhoA activity via a c-Src-dependent mechanism. Curr. Biol. 2000;10:719–722. - PubMed
-
- Astier A., Avraham H., Manie S.N., Groopman J., Canty T., Avraham S., Freedman A.S. The related adhesion focal tyrosine kinase is tyrosine phosphorylated after β1-integrin stimulation in B cells and binds to p130Cas . J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:228–232. - PubMed
-
- Avraham H., Park S.Y., Schinkmann K., Avraham S. RAFTK/Pyk2-mediated cellular signalling. Cell. Signal. 2000;12:123–133. - PubMed
-
- Calderwood D.A., Zent R., Grant R., Rees D.J., Hynes R.O., Ginsberg M.H. The talin head domain binds to integrin beta subunit cytoplasmic tails and regulates integrin activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:28071–28074. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

