The phagosome proteome: insight into phagosome functions
- PMID: 11149929
- PMCID: PMC2193653
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.152.1.165
The phagosome proteome: insight into phagosome functions
Abstract
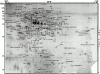
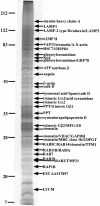
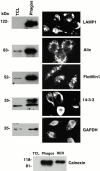
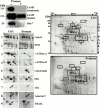
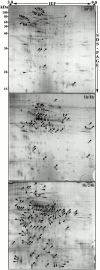
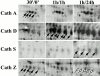
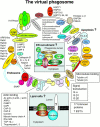
Phagosomes are key organelles for the innate ability of macrophages to participate in tissue remodeling, clear apoptotic cells, and restrict the spread of intracellular pathogens. To understand the functions of phagosomes, we initiated the systematic identification of their proteins. Using a proteomic approach, we identified >140 proteins associated with latex bead-containing phagosomes. Among these were hydrolases, proton pump ATPase subunits, and proteins of the fusion machinery, validating our approach. A series of unexpected proteins not previously described along the endocytic/phagocytic pathways were also identified, including the apoptotic proteins galectin3, Alix, and TRAIL, the anti-apoptotic protein 14-3-3, the lipid raft-enriched flotillin-1, the anti-microbial molecule lactadherin, and the small GTPase rab14. In addition, 24 spots from which the peptide masses could not be matched to entries in any database potentially represent new phagosomal proteins. The elaboration of a two-dimensional gel database of >160 identified spots allowed us to analyze how phagosome composition is modulated during phagolysosome biogenesis. Remarkably, during this process, hydrolases are not delivered in bulk to phagosomes, but are instead acquired sequentially. The systematic characterization of phagosome proteins provided new insights into phagosome functions and the protein or groups of proteins involved in and regulating these functions.
Figures
References
-
- Alvarez-Dominguez C., Stahl P.D. Increased expression of Rab5a correlates directly with accelerated maturation of Listeria monocytogenes phagosomes. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:11459–11462. - PubMed
-
- Berón W., Colombo M.I., Mayorga L.S., Stahl P.D. In vitro reconstitution of phagosome-endosome fusionevidence for regulation by heterotrimeric GTPases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1995;317:337–342. - PubMed
-
- Bickel P.E., Scherer P.E., Schnitzer J.E., Oh P., Lisanti M.P., Lodish H.F. Flotillin and epidermal surface antigen define a new family of caveolae-associated integral membrane proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1997;272:13793–13802. - PubMed
-
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J. Biol. Chem. 1981;256:1604–1607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

