Blockade of NGF-induced neurite outgrowth by a dominant-negative inhibitor of the egr family of transcription regulatory factors
- PMID: 11150318
- PMCID: PMC6762448
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-01-00045.2001
Blockade of NGF-induced neurite outgrowth by a dominant-negative inhibitor of the egr family of transcription regulatory factors
Abstract
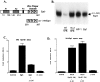
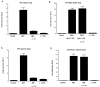
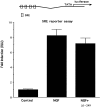
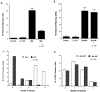
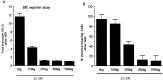
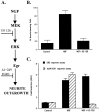
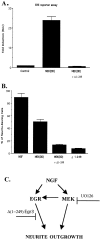
Although it is well established that members of the Egr family of transcription regulatory factors are induced in many neuronal plasticity paradigms, it is still unclear what role, if any, they play in this process. Because NGF stimulation of pheochromocytoma 12 cells elicits a robust induction of Egr family members, we have investigated their role in mediating long-term effects elicited by NGF in these cells by using the Egr zinc finger DNA-binding domain as a selective antagonist of Egr family-mediated transcription. We report that expression of this Egr inhibitor construct suppresses neurite outgrowth elicited by NGF but not by dibutyryl cAMP. To check that this Egr inhibitor construct does not act by blocking the MEK/ERK pathway, which is known to mediate NGF-induced neurite outgrowth, we confirmed that the Egr inhibitor construct does not block NGF activation of Elk1-mediated transcription, a response that is dependent on this pathway. Conversely, inhibition of MEK does not impair Egr family-mediated transcription. Thus, we conclude (1) that induction of Egr family members and activation of the MEK/ERK pathway by NGF are mediated by separate signaling pathways and (2) that both are required to trigger neurite outgrowth induced by NGF.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A dominant negative Egr inhibitor blocks nerve growth factor-induced neurite outgrowth by suppressing c-Jun activation: role of an Egr/c-Jun complex.J Neurosci. 2002 May 15;22(10):3845-54. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-10-03845.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12019303 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve growth factor- and epidermal growth factor-regulated gene transcription in PC12 pheochromocytoma and INS-1 insulinoma cells.Eur J Cell Biol. 2000 Dec;79(12):924-35. doi: 10.1078/0171-9335-00126. Eur J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 11152283
-
A dominant negative inhibitor of the Egr family of transcription regulatory factors suppresses cerebellar granule cell apoptosis by blocking c-Jun activation.J Neurosci. 2001 Aug 15;21(16):5893-901. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-16-05893.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11487612 Free PMC article.
-
The MEK-ERK-Egr-1 axis and its regulation in cardiovascular disease.Vascul Pharmacol. 2023 Dec;153:107232. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2023.107232. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Vascul Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37734428 Review.
-
Pathways of Egr-1-mediated gene transcription in vascular biology.Am J Pathol. 1999 Mar;154(3):665-70. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)65312-6. Am J Pathol. 1999. PMID: 10079243 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Identification of early growth response protein 1 (EGR-1) as a novel target for JUN-induced apoptosis in multiple myeloma.Blood. 2010 Jan 7;115(1):61-70. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-210526. Epub 2009 Oct 16. Blood. 2010. PMID: 19837979 Free PMC article.
-
Serum response factor mediated gene activity in physiological and pathological processes of neuronal motility.Front Mol Neurosci. 2011 Dec 6;4:49. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2011.00049. eCollection 2011. Front Mol Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 22164132 Free PMC article.
-
RAS and downstream RAF-MEK and PI3K-AKT signaling in neuronal development, function and dysfunction.Biol Chem. 2016 Mar;397(3):215-22. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2015-0270. Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26760308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upregulation of the neuron-specific K+/Cl- cotransporter expression by transcription factor early growth response 4.J Neurosci. 2006 Dec 27;26(52):13463-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4731-06.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 17192429 Free PMC article.
-
The basic region and leucine zipper transcription factor MafK is a new nerve growth factor-responsive immediate early gene that regulates neurite outgrowth.J Neurosci. 2002 Oct 15;22(20):8971-80. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-20-08971.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 12388604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abraham WC, Otani S. Macromolecules and the maintenance of long-term potentiation. In: Morrell F, editor. Kindling and synaptic plasticity, the legacy of Graham Goddard. Birkhauser; Boston: 1991. pp. 92–109.
-
- Ahn S, Ginty DD, Linden DJ. A late phase of cerebellar long-term depression requires activation of CaMKIV and CREB. Neuron. 1999;23:559–568. - PubMed
-
- Chapman NR, Perkins ND. Inhibition of the RelA(p65) NF-kB subunit by Egr-1. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:4719–4725. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
