Presynaptic kainate receptors regulate spinal sensory transmission
- PMID: 11150320
- PMCID: PMC6762455
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-01-00059.2001
Presynaptic kainate receptors regulate spinal sensory transmission
Abstract
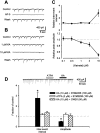
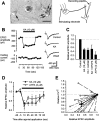
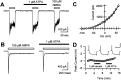
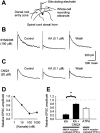
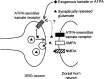
Small diameter dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons, which include cells that transmit nociceptive information into the spinal cord, are known to express functional kainate receptors. It is well established that exposure to kainate will depolarize C-fiber afferents arising from these cells. Although the role of kainate receptors on sensory afferents is unknown, it has been hypothesized that presynaptic kainate receptors may regulate glutamate release in the spinal cord. Here we show that kainate, applied at low micromolar concentrations in the presence of the AMPA-selective antagonist (RS)-4-(4-aminophenyl)-1, 2-dihydro-1-methyl-2-propyl-carbamoyl-6,7-methylenedioxyphthalazine++ +, suppressed spontaneous NMDA receptor-mediated EPSCs in cultures of spinal dorsal horn neurons. In addition, kainate suppressed EPSCs in dorsal horn neurons evoked by stimulation of synaptically coupled DRG cells in DRG-dorsal horn neuron cocultures. Interestingly, although the glutamate receptor subunit 5-selective kainate receptor agonist (RS)-2-alpha-amino-3-(3-hydroxy-5-tert-butylisoxazol-4-yl) propanoic acid (ATPA) (2 micrometer) was able to suppress DRG-dorsal horn synaptic transmission to a similar extent as kainate (10 micrometer), it had no effect on excitatory transmission between dorsal horn neurons. Agonist applications revealed a striking difference between kainate receptors expressed by DRG and dorsal horn neurons. Whereas DRG cell kainate receptors were sensitive to both kainate and ATPA, most dorsal horn neurons responded only to kainate. Finally, in recordings from dorsal horn neurons in spinal slices, kainate and ATPA were able to suppress NMDA and AMPA receptor-mediated EPSCs evoked by dorsal root fiber stimulation. Together, these data suggest that kainate receptor agonists, acting at a presynaptic locus, can reduce glutamate release from primary afferent sensory synapses.
Figures

References
-
- Ault B, Hildebrand LM. Activation of nociceptive reflexes by peripheral kainate receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993;265:927–932. - PubMed
-
- Bekkers JM, Stevens CF. Presynaptic mechanism for long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1990;346:724–729. - PubMed
-
- Bortolotto ZA, Clarke VR, Delany CM, Parry MC, Smolders I, Vignes M, Ho KH, Miu P, Brinton BT, Fantaske R, Ogden A, Gates M, Ornstein PL, Lodge D, Bleakman D, Collingridge GL. Kainate receptors are involved in synaptic plasticity. Nature. 1999;402:297–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
