Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in cortical neurons is regulated by striatal target area
- PMID: 11150327
- PMCID: PMC6762434
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-01-00117.2001
Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in cortical neurons is regulated by striatal target area
Abstract
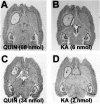
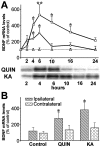
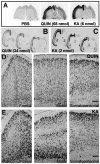
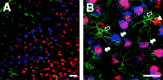
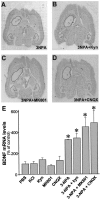
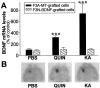
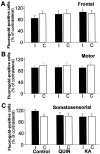
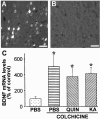
Changes in BDNF expression after different types of brain insults are related to neuroprotection, stimulation of sprouting, and synaptic reorganization. In the cerebral cortex, an autocrine-paracrine mechanism for BDNF has been proposed because the distribution patterns of BDNF and TrkB expression are almost identical. Moreover, cortical BDNF is anterogradely transported to the striatum, suggesting a role of BDNF in the functional interaction between the two brain regions. Here we have examined the expression of this neurotrophin in the cerebral cortex after various striatal lesions. Intrastriatal injection of quinolinate, kainate, 3-nitropropionic acid, or colchicine increased BDNF mRNA levels in cerebral cortex. In contrast, stimulation of neuronal activity in the striatum did not change cortical BDNF expression. Both excitatory amino acids increased BDNF expression in neurons of cortical layers II/III, V, and VI that project to the striatum. Moreover, grafting a BDNF-secreting cell line prevented both the loss of striatal neurons and the cortical upregulation of BDNF induced by excitotoxins. Because retrograde transport in the corticostriatal pathway was intact after striatal lesions, our results suggest that striatal damage upregulates endogenous BDNF in corticostriatal neurons by a transneuronal mechanism, which may constitute a protective mechanism for striatal and/or cortical cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, neurotrophin-3, and neurotrophin-4/5 prevent the death of striatal projection neurons in a rodent model of Huntington's disease.J Neurochem. 2000 Nov;75(5):2190-9. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0752190.x. J Neurochem. 2000. PMID: 11183872
-
Divergent regulatory mechanisms governing BDNF mRNA expression in cerebral cortex and substantia nigra in response to striatal target ablation.Exp Neurol. 2005 Mar;192(1):142-55. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2004.11.005. Exp Neurol. 2005. PMID: 15698628
-
Astrocytes from cortex and striatum show differential responses to mitochondrial toxin and BDNF: implications for protection of striatal neurons expressing mutant huntingtin.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Oct 6;17(1):290. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01965-4. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 33023623 Free PMC article.
-
Corticostriatal BDNF and alcohol addiction.Brain Res. 2015 Dec 2;1628(Pt A):60-7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.03.025. Epub 2015 Mar 21. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25801118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in Huntington's disease.Prog Neurobiol. 2007 Apr;81(5-6):294-330. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2007.01.003. Epub 2007 Feb 9. Prog Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17379385 Review.
Cited by
-
Regional differences in neurotrophin availability regulate selective expression of VGF in the developing limbic cortex.J Neurosci. 2001 Dec 1;21(23):9315-24. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-23-09315.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11717365 Free PMC article.
-
BDNF Overexpression Enhances Neuronal Activity and Axonal Growth in Human iPSC-Derived Neural Cultures.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 27;26(15):7262. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157262. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806396 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of BDNF in Pax2 Lineage-Derived Interneuron Precursors in the Hindbrain Hampers the Proportion of Excitation/Inhibition, Learning, and Behavior.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Mar 26;14:642679. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.642679. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33841098 Free PMC article.
-
Smith-Magenis syndrome protein RAI1 regulates body weight homeostasis through hypothalamic BDNF-producing neurons and neurotrophin downstream signalling.Elife. 2023 Nov 13;12:RP90333. doi: 10.7554/eLife.90333. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37956053 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy and apoptosis cascade: which is more prominent in neuronal death?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec;78(24):8001-8047. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04004-4. Epub 2021 Nov 6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34741624 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Altar CA, Cai N, Bliven T, Juhasz M, Conner JM, Acheson AL, Lindsay RM, Wiegand SJ. Anterograde transport of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its role in the brain. Nature. 1997;389:856–860. - PubMed
-
- Arenas E, Persson H. NT-3 prevents the death of adult central noradrenergic neurons in vivo. Nature. 1994;367:368–371. - PubMed
-
- Beal MF, Kowall NW, Ellison DW, Mazurek MF, Swartz KJ, Martin JB. Replication of the neurochemical characteristics of Huntington's disease by quinolinic acid. Nature. 1986;321:168–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
