An evolutionarily conserved transmembrane protein that is a novel downstream target of neurotrophin and ephrin receptors
- PMID: 11150334
- PMCID: PMC6762419
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-01-00176.2001
An evolutionarily conserved transmembrane protein that is a novel downstream target of neurotrophin and ephrin receptors
Abstract
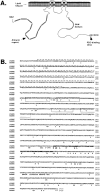
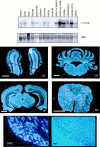
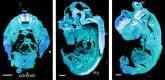
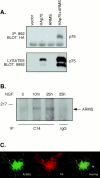
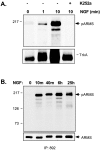
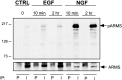
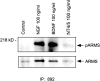
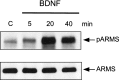
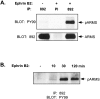
Appropriate development of nervous system connectivity involves a variety of processes, including neuronal life-and-death decisions, differentiation, axon guidance and migration, and synaptogenesis. Although these activities likely require specialized signaling events, few substrates unique to these neurotrophic functions have been identified. Here we describe the cloning of ankyrin repeat-rich membrane spanning (ARMS), which encodes a novel downstream target of neurotrophin and ephrin receptor tyrosine kinases, Trk and Eph, respectively. The amino acid sequence of ARMS is highly conserved from nematode to human, suggesting an evolutionarily conserved role for this protein. The ARMS protein consists of 1715 amino acids containing four putative transmembrane domains, multiple ankyrin repeats, a sterile alpha motif domain, and a potential PDZ-binding motif. In the rat, ARMS is specifically expressed in the developing nervous system and in highly plastic areas of the adult brain, regions enriched in Trks and Eph receptors. ARMS can physically associate with TrkA and p75 neurotrophin receptors. Moreover, endogenous ARMS protein is tyrosine phosphorylated after neurotrophin treatment of pheochromocytoma 12 cells and primary hippocampal neurons or ephrin B treatment of NG108-15 cells, demonstrating that ARMS is a downstream target for both neurotrophin and ephrin receptors.
Figures

References
-
- Aibel L, Martin-Zanca D, Perez P, Chao MV. Functional expression of TrkA receptors in hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci Res. 1998;54:424–431. - PubMed
-
- Barker PA, Shooter EM. Disruption of NGF binding to the low affinity neurotrophin receptor p75LNTR reduces NGF binding to TrkA on PC12 cells. Brain Res. 1994;664:155–166. - PubMed
-
- Berg MM, Sternberg DW, Parada LF, Chao MV. K-252a inhibits nerve growth factor-induced trk proto-oncogene tyrosine phosphorylation and kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:13–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
