Developmental expression of retinal cone cGMP-gated channels: evidence for rapid turnover and trophic regulation
- PMID: 11150339
- PMCID: PMC6762422
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-01-00221.2001
Developmental expression of retinal cone cGMP-gated channels: evidence for rapid turnover and trophic regulation
Abstract
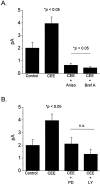
The cyclic GMP-gated cationic channels of vertebrate photoreceptors are essential for visual phototransduction. We have examined the developmental regulation of cGMP-gated channels in morphologically identified cones in the chick retina. Expression of cone-type cGMP-gated channel mRNA can be detected at embryonic day 6 (E6), but expression of functional channels, as accessed by patch-clamp recordings, cannot be detected until E8. Plasma membrane channels in embryonic cones have a high turnover rate because inhibition of protein synthesis or disruption of the Golgi apparatus causes an almost complete loss of functional cGMP-gated channels within 12 hr. Different subpopulations of cones begin to express functional channels at different developmental stages, but all cones express channels by E10. Expression of cGMP-gated channels in at least one cone subpopulation appears to require one or more soluble differentiation factors, which are presumably present in the normal microenvironment of the developing retina. Application of chick embryo extract (CEE), a rich source of trophic factors, causes marked stimulation of cGMP-gated channel expression in chick cones at E8, but not at E6. Inhibition of MAP kinase (Erk) signaling using PD98059, or inhibition of PI3 kinase signaling by LY294002, blocked the stimulatory effects of CEE on E8 cones. Several recombinant trophic factors were also tested, but none could mimic the stimulatory effects of CEE on channel expression. In summary, the developmental expression of cGMP-gated cationic channels in embryonic cones appears to be regulated by epigenetic factors. The ability of cones to respond to these epigenetic factors is also developmentally regulated.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Circadian regulation of cGMP-gated cationic channels of chick retinal cones. Erk MAP Kinase and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II.Neuron. 2001 Jan;29(1):255-66. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(01)00195-7. Neuron. 2001. PMID: 11182096
-
Tuning outer segment Ca2+ homeostasis to phototransduction in rods and cones.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;514:179-203. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0121-3_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002. PMID: 12596922 Review.
-
Tyrosine phosphorylation of cGMP-gated ion channels is under circadian control in chick retina photoreceptors.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007 Feb;48(2):901-6. doi: 10.1167/iovs.06-0824. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007. PMID: 17251493 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian phase-dependent modulation of cGMP-gated channels of cone photoreceptors by dopamine and D2 agonist.J Neurosci. 2003 Apr 15;23(8):3145-53. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-08-03145.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12716922 Free PMC article.
-
cGMP Signaling in Photoreceptor Degeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 7;24(13):11200. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311200. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446378 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 and -2 enhance the ligand sensitivity of photoreceptor cyclic nucleotide-gated channels.Channels (Austin). 2012 May-Jun;6(3):181-96. doi: 10.4161/chan.20904. Epub 2012 May 1. Channels (Austin). 2012. PMID: 22699690 Free PMC article.
-
Chicken embryos as a potential new model for early onset type I diabetes.J Diabetes Res. 2014;2014:354094. doi: 10.1155/2014/354094. Epub 2014 Jul 13. J Diabetes Res. 2014. PMID: 25133191 Free PMC article.
-
Nitric oxide regulates angiogenesis through a functional switch involving thrombospondin-1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Sep 13;102(37):13147-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502979102. Epub 2005 Sep 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16141331 Free PMC article.
-
Somatostatin peptides produce multiple effects on gating properties of native cone photoreceptor cGMP-gated channels that depend on circadian phase and previous illumination.J Neurosci. 2007 Nov 7;27(45):12168-75. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3541-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17989283 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler R. Developmental predetermination of the structural and molecular polarization of photoreceptor cells. Dev Biol. 1986;117:520–527. - PubMed
-
- Adler R. Determination of cellular types in the retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1993;34:1677–1682. - PubMed
-
- Adler R, Hatlee M. Plasticity and differentiation of embryonic retinal cells after terminal mitosis. Science. 1989;243:391–393. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad I, Redmond LJ, Barnstable CJ. Developmental and tissue-specific expression of the rod photoreceptor cGMP-gated ion channel gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990;173:463–470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
