Enhanced cortical extracellular levels of cholecystokinin-like material in a model of anticipation of social defeat in the rat
- PMID: 11150343
- PMCID: PMC6762450
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-01-00262.2001
Enhanced cortical extracellular levels of cholecystokinin-like material in a model of anticipation of social defeat in the rat
Abstract
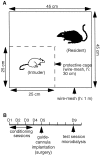
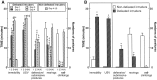
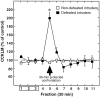
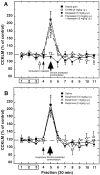
The involvement of cholecystokinin (CCK) in the mechanisms of stress and/or anxiety was assessed by in vivo microdialysis in rats subjected to a social stress paradigm. During the initial 30 min period of each conditioning session, a male Sprague Dawley rat (intruder) was placed in a protective cage inside the cage of a male Tryon Maze Dull rat (resident), allowing unrestricted visual, olfactory, and auditory contacts but precluding close physical contact between them. During the following 15 min period, both the protective cage and the resident were removed (nondefeated intruders) or only the protective cage was removed allowing the resident to attack the intruder (defeated rats). This procedure was repeated once daily for 4 d. On the fifth day, a guide cannula was implanted into the prefrontal cortex of intruders. During a single 30 min test session, performed 4 d later, intruders were subjected to only the 30 min protected confrontation to the resident. Anxiety-like behavior (immobility, ultrasonic vocalizations, and defensive postures), associated with an increase (approximately +100% above baseline) in cortical outflow of CCK-like material (CCKLM), were observed in defeated intruders. Pretreatment with diazepam (5 mg/kg, i.p.), but not buspirone (0.5-2 mg/kg, i.p.), prevented both the anxiety-related behavior and CCKLM overflow. The selective CCK-B receptor antagonist CI-988 (2 mg/kg, i.p.) reduced the anxiety-like behavior without affecting the increase in CCKLM outflow. These data indicate that anticipation of social defeat induces a marked activation of cortical CCKergic neurons associated with anxiety-related behaviors in rats.
Figures
References
-
- Adamec RE, Shallow T, Budgel J. Blockade of CCKB but not CCKA receptors before and after the stress of predator exposure prevents lasting increases in anxiety-like behavior: implications for anxiety associated with posttraumatic stress disorder. Behav Neurosci. 1997;111:435–449. - PubMed
-
- Albonetti ME, Farabollini F. Social stress by repeated defeat: effects on social behaviour and emotionality. Behav Brain Res. 1994;62:187–193. - PubMed
-
- Becker C, Hamon M, Benoliel J-J. Prevention by 5-HT1A receptor agonists of restraint stress- and yohimbine-induced release of cholecystokinin in the frontal cortex of the freely moving rat. Neuropharmacology. 1999;38:525–532. - PubMed
-
- Beinfeld MC, Meyer DK, Eskay RL, Jensen RT, Brownstein MJ. The distribution of cholecystokinin immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat as determined by radioimmunoassay. Brain Res. 1981;212:51–57. - PubMed
-
- Benoliel J-J, Bourgoin S, Mauborgne A, Pohl M, Legrand JC, Hamon M, Cesselin F. GABA, acting at both GABAA and GABAB receptors, inhibits the release of cholecystokinin-like material from the rat spinal cord in vitro. Brain Res. 1992;590:255–262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
