Protein kinase SGK mediates survival signals by phosphorylating the forkhead transcription factor FKHRL1 (FOXO3a)
- PMID: 11154281
- PMCID: PMC86685
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.3.952-965.2001
Protein kinase SGK mediates survival signals by phosphorylating the forkhead transcription factor FKHRL1 (FOXO3a)
Abstract
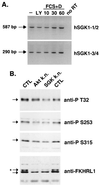
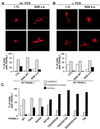
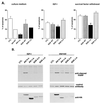
Serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinases (SGKs) form a novel family of serine/threonine kinases that are activated in response to a variety of extracellular stimuli. SGKs are related to Akt (also called PKB), a serine/threonine kinase that plays a crucial role in promoting cell survival. Like Akt, SGKs are activated by the phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3K) and translocate to the nucleus upon growth factor stimulation. However the physiological substrates and cellular functions of SGKs remained to be identified. We hypothesized that SGKs regulate cellular functions in concert with Akt by phosphorylating common targets within the nucleus. The best-characterized nuclear substrates of Akt are transcription factors of the Forkhead family. Akt phosphorylates Forkhead transcription factors such as FKHRL1, leading to FKHRL1's exit from the nucleus and the consequent shutoff of FKHRL1 target genes. We show here that SGK1, like Akt, promotes cell survival and that it does so in part by phosphorylating and inactivating FKHRL1. However, SGK and Akt display differences with respect to the efficacy with which they phosphorylate the three regulatory sites on FKHRL1. While both kinases can phosphorylate Thr-32, SGK displays a marked preference for Ser-315 whereas Akt favors Ser-253. These findings suggest that SGK and Akt may coordinately regulate the function of FKHRL1 by phosphorylating this transcription factor at distinct sites. The efficient phosphorylation of these three sites on FKHRL1 by SGK and Akt appears to be critical to the ability of growth factors to suppress FKHRL1-dependent transcription, thereby preventing FKHRL1 from inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. These findings indicate that SGK acts in concert with Akt to propagate the effects of PI3K activation within the nucleus and to mediate the biological outputs of PI3K signaling, including cell survival and cell cycle progression.
Figures
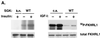
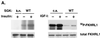
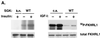





References
-
- Alessi D R, Caudwell F B, Andjelkovic M, Hemmings B A, Cohen P. Molecular basis for the substrate specificity of protein kinase B; comparison with MAPKAP kinase-1 and p70 S6 kinase. FEBS Lett. 1996;399:333–338. - PubMed
-
- Alessi D R, Kozlowski M T, Weng Q P, Morrice N, Avruch J. 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1) phosphorylates and activates the p70 S6 kinase in vivo and in vitro. Curr Biol. 1998;8:69–81. - PubMed
-
- Alliston T N, Maiyar A C, Buse P, Firestone G L, Richards J S. Follicle stimulating hormone-regulated expression of serum/glucocorticoid-inducible kinase in rat ovarian granulosa cells: a functional role for the Sp1 family in promoter activity. Mol Endocrinol. 1997;11:1934–1949. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez de la Rosa D, Zhang P, Naray-Fejes-Toth A, Fejes-Toth G, Canessa C M. The serum and glucocorticoid kinase sgk increases the abundance of epithelial sodium channels in the plasma membrane of Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:37834–37839. - PubMed
-
- Bellacosa A, Testa J R, Staal S P, Tsichlis P N. A retroviral oncogene, akt, encoding a serine threonine kinase containing a SH2-like region. Science. 1991;254:274–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
