Sensitivity of quantitative (1)H magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain in detecting early neuronal damage in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 11156541
- PMCID: PMC1753471
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.60.2.106
Sensitivity of quantitative (1)H magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain in detecting early neuronal damage in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
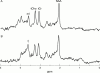
Objective: To quantify N-acetylaspartate (NAA), total creatines (tCr), total cholines (tCho), and myo-inositol (mI) levels in normal and abnormal appearing white matter of patients with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus (NPSLE) in order to determine the specific changes in metabolite concentrations.
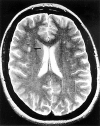
Methods: Axial proton density and T(2) weighted magnetic resonance images, and short echo time (TE 30 ms) (1)H spectra were acquired with a GE SIGNA 1.5 T magnetic resonance system. Concentrations of NAA, tCr, tCho, and mI were determined, using brain tissue water as a reference, from nine patients (seven female, mean age 40.3 years, range 16-65) with NPSLE and eight healthy women (mean age 43 years, range 31-65).
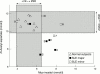
Results: A significant rise of tCho (12.4%, p<0.05) and mI (31.4%, p<0.005) and a significant reduction in NAA (-12%, p<0.05) was found in normal appearing white matter compared with controls. Analysis according to severity of the clinical NPSLE features (subgrouped as major or minor) showed that SLE major had reduced NAA compared with SLE minor (-18.4%, p<0.05) and controls (-20%, p<0.005). The SLE major group showed a significant rise of mI (32%, p<0.01) and the SLE minor group a significant increase in tCho (18.6%, p<0.05) compared with controls. Longitudinal analysis of brain metabolites in normal appearing white matter showed consistent abnormalities in NAA, tCho, and mI in a patient with stable clinical features and a constant rise of tCho, but transient rise of mI was seen during a flare of disease in another patient.
Conclusion: Quantitative (1)H magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) suggests a particular course of neurometabolite changes that precedes irreversible reductions in NAA and permanent neuronal loss. Initially, in patients with SLE minor, there is a significant rise in tCho and a trend (reversible) for mI also to be raised. In patients with SLE major the NAA is significantly and permanently reduced and mI is significantly raised, whereas the tCho levels are near normal. Further investigations are needed to determine how specific MRS is as a clinical marker for brain disturbance in SLE.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reduced Insular Glutamine and N-acetylaspartate in systemic lupus erythematosus: a single-voxel (1)H-MR spectroscopy study.Acad Radiol. 2013 Oct;20(10):1286-96. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2013.07.011. Acad Radiol. 2013. PMID: 24029061 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of reversible axonal dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus: a proton MRS study.Brain. 2005 Dec;128(Pt 12):2933-40. doi: 10.1093/brain/awh646. Epub 2005 Sep 29. Brain. 2005. PMID: 16195241
-
Neurometabolite markers of cerebral injury in the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome of systemic lupus erythematosus.Stroke. 1998 Nov;29(11):2254-60. doi: 10.1161/01.str.29.11.2254. Stroke. 1998. PMID: 9804631
-
Meta-analysis of brain metabolite differences in HIV infection.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;28:102436. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102436. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 33383609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Alzheimer's disease and magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the hippocampus].Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2001 Dec;59(4):865-70. doi: 10.1590/s0004-282x2001000600006. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2001. PMID: 11733829 Review. Portuguese.
Cited by
-
Chance, genetics, and the heterogeneity of disease and pathogenesis in systemic lupus erythematosus.Semin Immunopathol. 2014 Sep;36(5):495-517. doi: 10.1007/s00281-014-0440-x. Epub 2014 Aug 8. Semin Immunopathol. 2014. PMID: 25102991 Review.
-
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy may predict future brain lesions in SLE patients: a functional multi-imaging approach and follow up.Ann Rheum Dis. 2005 Jul;64(7):1022-7. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.026773. Epub 2005 Jan 7. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. PMID: 15640271 Free PMC article.
-
MRI and 2D-CSI MR spectroscopy of the brain in the evaluation of patients with acute onset of neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus.Neuroradiology. 2005 Aug;47(8):576-85. doi: 10.1007/s00234-005-1371-y. Epub 2005 Jul 9. Neuroradiology. 2005. PMID: 16007461
-
Reduced Insular Glutamine and N-acetylaspartate in systemic lupus erythematosus: a single-voxel (1)H-MR spectroscopy study.Acad Radiol. 2013 Oct;20(10):1286-96. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2013.07.011. Acad Radiol. 2013. PMID: 24029061 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the impact of neuro-inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis.Front Neurosci. 2014 Nov 6;8:357. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00357. eCollection 2014. Front Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25414636 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

