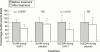UVA-1 cold light treatment of SLE: a double blind, placebo controlled crossover trial
- PMID: 11156542
- PMCID: PMC1753460
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.60.2.112
UVA-1 cold light treatment of SLE: a double blind, placebo controlled crossover trial
Abstract
Objective: Treatment of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) often implies strong drugs with possibly serious side effects. Thus there is a need for new immunosuppressive treatments. Long wave ultraviolet A (UVA-1) cold light therapy is an anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory treatment with a possible systemic effect and few side effects. In the current study low dose UVA-1 cold light treatment was tested to determine whether it reduces disease activity in SLE.
Methods: Eleven patients with SLE were treated with UVA-1 cold light treatment and a placebo light treatment in a double blind, placebo controlled, crossover study. In two consecutive 12 week periods the patients were treated in the first three weeks with UVA-1 and placebo treatment or vice versa. The primary variables were the SLE Disease Activity Index (SLEDAI) and SLE Activity Measure (SLAM).
Results: The mean SLAM and SLEDAI showed a significant decrease of 30.4% (p=0.0005) and 37.9% (p=0.016) respectively after three weeks of UVA-1 and a non-significant decline of 9.3% (p=0.43) and 12.2% (p=0.54) respectively after three weeks of placebo treatment. In this small trial the difference in reduction of the disease activity indices during UVA-1 compared with during placebo treatment failed to reach the conventional border of significance (p=0.07). The total score of quality of life measure RAND-36 did not improve significantly, but the subscore for vitality did improve.
Conclusion: Low dose UVA-1 cold light treatment was strongly suggestive of lowering disease activity in this double blind placebo controlled study, and no side effects occurred.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical