Esculetin inhibits cartilage resorption induced by interleukin 1alpha in combination with oncostatin M
- PMID: 11156550
- PMCID: PMC1753478
- DOI: 10.1136/ard.60.2.158
Esculetin inhibits cartilage resorption induced by interleukin 1alpha in combination with oncostatin M
Abstract
Objective: To determine if a new inhibitor, esculetin (EST), can block resorption of cartilage.
Methods: Interleukin 1alpha (IL1alpha, 0.04-5 ng/ml) and oncostatin M (OSM, 0.4-50 ng/ml) were used to stimulate the release of proteoglycan and collagen from bovine nasal cartilage and human articular cartilage in explant culture. Proteoglycan and collagen loss were assessed by dimethylmethylene blue and hydroxyproline assays, respectively. Collagenase levels were measured by assay of bioactivity and by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The effects of EST on the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) in the transformed human chondrocyte cell line T/C28a4 were assessed by northern blot analysis. TIMP-1 protein levels were assayed by ELISA. The effect of EST on the MMP-1 promoter was assessed using a promoter-luciferase construct in transient transfection studies.
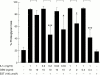
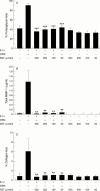
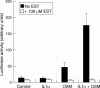
Results: EST inhibited proteoglycan and collagen resorption in a dose dependent manner with significant decreases seen at 66 microM and 100 microM EST, respectively. Collagenolytic activity was significantly decreased in bovine nasal cartilage cultures. In human articular cartilage, EST also inhibited IL1alpha + OSM stimulated resorption and decreased MMP-1 levels. TIMP-1 levels were not altered compared with controls. In T/C28a4 chondrocytes the IL1alpha + OSM induced expression of MMP-1, MMP-3, and MMP-13 mRNA was reduced to control levels by 250 microM EST. TIMP-1 mRNA levels were unaffected by EST treatment. All cytokine stimulation of an MMP-1 luciferase-promoter construct was lost in the presence of the inhibitor.
Conclusion: EST inhibits degradation of bovine nasal cartilage and human articular cartilage stimulated to resorb with IL1alpha + OSM.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1 blocks collagen release and down regulates matrix metalloproteinase-1, -3, -8, and -13 mRNA expression in bovine nasal cartilage stimulated with oncostatin M in combination with interleukin 1alpha.Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Mar;60(3):254-61. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.3.254. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001. PMID: 11171688 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 13 blocks the release of collagen from bovine nasal cartilage treated with proinflammatory cytokines.Ann Rheum Dis. 2001 Feb;60(2):150-7. doi: 10.1136/ard.60.2.150. Ann Rheum Dis. 2001. PMID: 11156549 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic effects of glycoprotein 130 binding cytokines in combination with interleukin-1 on cartilage collagen breakdown.Arthritis Rheum. 2001 Jul;44(7):1620-32. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200107)44:7<1620::AID-ART285>3.0.CO;2-B. Arthritis Rheum. 2001. PMID: 11465713
-
Retinoic acid and oncostatin M combine to promote cartilage degradation via matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in bovine but not human chondrocytes.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006 Aug;45(8):958-65. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kel024. Epub 2006 Feb 8. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006. PMID: 16467367
-
Human nasal cartilage responds to oncostatin M in combination with interleukin 1 or tumour necrosis factor alpha by the release of collagen fragments via collagenases.Ann Rheum Dis. 2006 Feb;65(2):184-90. doi: 10.1136/ard.2004.033480. Epub 2005 Jun 23. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. PMID: 15975972 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Esculetin Attenuates the Migration and Invasion of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Attenuating Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity and Strengthening Tight Junctions.J Cancer Prev. 2025 Jun 30;30(2):111-117. doi: 10.15430/JCP.25.014. J Cancer Prev. 2025. PMID: 40621158 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical potential of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in the rheumatic disorders.Drugs Aging. 2001;18(2):87-99. doi: 10.2165/00002512-200118020-00002. Drugs Aging. 2001. PMID: 11346130 Review.
-
Pharmacological and Therapeutic Applications of Esculetin.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 20;23(20):12643. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012643. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Esculetin reduces leukotriene B4 level in plasma of rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis.Reumatologia. 2016;54(4):161-164. doi: 10.5114/reum.2016.62469. Epub 2016 Oct 5. Reumatologia. 2016. PMID: 27826169 Free PMC article.
-
Novel missense ACAN gene variants linked to familial osteochondritis dissecans cluster in the C-terminal globular domain of aggrecan.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 25;12(1):5215. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09211-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35338222 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

