Protective effects of a new stable, highly active SOD mimetic, M40401 in splanchnic artery occlusion and reperfusion
- PMID: 11156557
- PMCID: PMC1572533
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703775
Protective effects of a new stable, highly active SOD mimetic, M40401 in splanchnic artery occlusion and reperfusion
Abstract
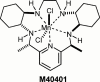
1. Splanchnic artery occlusion shock (SAO) causes an enhanced formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which contribute to the pathophysiology of shock. Here we have investigated the effects of M40401, a new S:,S:-dimethyl substituted biscyclohexylpyridine Mn-based superoxide dismutase mimetic (SODm, k(cat)=1.2x10(+9) M(-1) s(-1) at pH=7.4), in rats subjected to SAO shock. 2. Treatment of rats with M40401 (applied at 0.25, 2.5 or 25 microg kg(-1), 15 min prior to reperfusion), attenuated the mean arterial blood and the migration of polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) caused by SAO-shock. M40401 also attenuated the ileum injury (histology) as well as the increase in the tissue levels of myeloperoxidase (MPO) and malondialdehyde (MDA) caused by SAO shock in the ileum. 3. Immunohistochemical analysis for nitrotyrosine revealed a positive staining in ileum from SAO-shocked rats. The degree of staining for nitrotyrosine was markedly reduced in tissue sections obtained from SAO-shocked rats which had received M40401. Reperfused ileum tissue sections from SAO-shocked rats showed positive staining for P-selectin and for anti-intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM-1) in the vascular endothelial cells. M40401 treatment markedly reduced the intensity and degree of P-selectin and ICAM-1 in tissue sections from SAO-shocked rats. M40401 treatment significantly improved survival. 4. Additionally, the very high catalytic activity of this new mimetic (comparable to the native human Cu/Zn SOD enzyme and exceeding the activity of the human Mn SOD enzyme) translates into a very low dose ( approximately microg kg(-1)) required to afford protection in this SAO model of ischemia reperfusion injury. 5. Taken together, our results clearly demonstrate that M40401 treatment exerts a protective effect, and part of this effect may be due to inhibition of the expression of adhesion molecules and peroxynitrite-related pathways with subsequent reduction of neutrophil-mediated cellular injury.
Figures

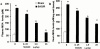

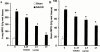




Similar articles
-
Effects of n-acetylcysteine in a rat model of ischemia and reperfusion injury.Cardiovasc Res. 2000 Aug 18;47(3):537-48. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(00)00018-3. Cardiovasc Res. 2000. PMID: 10963726
-
Beneficial effects of peroxynitrite decomposition catalyst in a rat model of splanchnic artery occlusion and reperfusion.FASEB J. 2000 Jun;14(9):1061-72. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.14.9.1061. FASEB J. 2000. PMID: 10834927
-
IL-6 knock-out mice exhibit resistance to splanchnic artery occlusion shock.J Leukoc Biol. 1999 Sep;66(3):471-80. doi: 10.1002/jlb.66.3.471. J Leukoc Biol. 1999. PMID: 10496318
-
Beneficial effects of melatonin in a rat model of splanchnic artery occlusion and reperfusion.J Pineal Res. 2000 Jan;28(1):52-63. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-079x.2000.280108.x. J Pineal Res. 2000. PMID: 10626602
-
Mechanisms of the protective effects of transforming growth factor-beta in reperfusion injury.Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Sep 12;42(7):1323-7. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90441-7. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991. PMID: 1930256 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effects of relaxin in ischemia/reperfusion-induced intestinal injury due to splanchnic artery occlusion.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Aug;148(8):1124-32. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706811. Epub 2006 Jul 17. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16847443 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta inhibition attenuates the development of ischaemia/reperfusion injury of the gut.Intensive Care Med. 2007 May;33(5):880-893. doi: 10.1007/s00134-007-0595-1. Epub 2007 Mar 24. Intensive Care Med. 2007. Retraction in: Intensive Care Med. 2024 Jun;50(6):1019. doi: 10.1007/s00134-024-07320-y. PMID: 17384932 Retracted.
-
On the selectivity of superoxide dismutase mimetics and its importance in pharmacological studies.Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Oct;140(3):445-60. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705430. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14522841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) attenuates lung injury induced by intestinal ischemia/reperfusion in rats: roles of oxidative stress and nitric oxide.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Jan 14;13(2):299-305. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i2.299. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17226913 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress and redox modulation potential in type 1 diabetes.Clin Dev Immunol. 2011;2011:593863. doi: 10.1155/2011/593863. Epub 2011 May 18. Clin Dev Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21647409 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ALTURA B.M., GEBREWOLDA A., BURTON R.W. Reactive hyperaemic responses of single arterioles are attenuated markedly after intestinal ischemia, endotoxemia and traumatic shock: possible role of endothelial cells. Microcirc. Endothelium Lymphatics. 1985;2:3–14. - PubMed
-
- AMBROSIO G., FLAHERTY J.T. Effects of the superoxide radical scavenger superoxide dismutase, and of the hydroxyl radical scavenger mannitol, on reperfusion injury in isolated rabbit hearts. Cardiovasc. Drugs. Ther. 1992;6:623–632. - PubMed
-
- BECKMAN J.S., CROW L.P. Pathological implications of nitric oxide, superoxide and peroxynitrite formation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1993;21:330–334. - PubMed
-
- BITTERMANN H., AOKI N., LEFER A.M. Anti-shock effects of human superoxide dismutase in splanchnic occlusion shock. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1988;188:256–271. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

