Sumatriptan elicits both constriction and dilation in human and bovine brain intracortical arterioles
- PMID: 11156561
- PMCID: PMC1572524
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703763
Sumatriptan elicits both constriction and dilation in human and bovine brain intracortical arterioles
Abstract
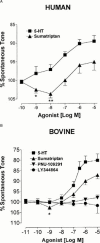
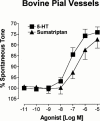
1. Little is known about serotonin (5-HT) receptors present on brain microvessels that are innervated by brainstem serotonergic neurons. Using 5-HT, sumatriptan and subtype selective 5-HT(1) receptor agonists and/or the 5-HT(1) receptor antagonist GR127935, we characterized the 5-HT receptors involved in regulating microvascular tone of pressurized intracortical arterioles (approximately 40--50 microm) isolated from human and bovine cerebral cortex. The role of nitric oxide (NO) on these responses was assessed with the N(omega)-nitro-L-arginine (L-NNA, 10(-5) M), an inhibitor of NO synthesis. Bovine pial arteries were studied for comparative purposes. 2. At spontaneous tone, 5-HT induced a dose-dependent constriction of human and bovine microarteries (respective pD(2) values of 7.3+/-0.2 and 6.9+/-0.1); a response potently inhibited by GR127935 (pIC(50) value of 8.5+/-0.1) in bovine microvessels. 3. In both species, the 5-HT(1) receptor agonist sumatriptan induced a biphasic response consisting of a small but significant dilation at low concentrations (1 and/or 10 nM) followed by a constriction at higher doses (pD(2) for contraction of 6.9+/-0.1 and 6.6+/-0.2 in human and bovine vessels, respectively). Pre-incubation with L-NNA abolished the sumatriptan-induced dilation and significantly shifted the dose-response of the constriction curve to the left. In contrast, the selective 5-HT(1D) (PNU-109291) and 5-HT(1F) (LY344864) receptor agonists were devoid of any vasomotor effect. 4. In bovine pial vessels, 5-HT and sumatriptan elicited potent constrictions (respective pD(2) of 7.2+/-0.1 and 6.6+/-0.1), a weak dilation being occasionally observed at low sumatriptan concentrations. 5. A significant negative correlation was observed between pial and intracortical vessels diameter and the extent of the dilatory response to 10(-9) M sumatriptan. Together, these results indicate that sumatriptan, most likely via activation of distinctly localized microvascular 5-HT(1B) receptors, can induce a constriction and/or a dilation which is sensitive to inhibition of NO synthesis and dependent on the size and, possibly, the existing tone of the vessels.
Figures



Similar articles
-
No contractile effect for 5-HT1D and 5-HT1F receptor agonists in human and bovine cerebral arteries: similarity with human coronary artery.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Feb;129(3):501-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703081. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10711348 Free PMC article.
-
Muscarinic--but not nicotinic--acetylcholine receptors mediate a nitric oxide-dependent dilation in brain cortical arterioles: a possible role for the M5 receptor subtype.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000 Feb;20(2):298-305. doi: 10.1097/00004647-200002000-00011. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2000. PMID: 10698067
-
Involvement of 5-HT(1B/1D) and 5-HT2A receptors in 5-HT-induced contraction of endothelium-denuded rabbit epicardial coronary arteries.Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Nov;122(5):875-84. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701470. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9384503 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT receptors mediating external carotid vasoconstriction in vagosympathectomized dogs.Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1999 Dec;20(12):1057-67. Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao. 1999. PMID: 11216445 Review.
-
Migraine: pathophysiology, pharmacology, treatment and future trends.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2003 Mar;1(1):71-84. doi: 10.2174/1570161033386826. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 15320857 Review.
Cited by
-
5-HT7 receptor-mediated dilatation in the middle meningeal artery of anesthetized rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Mar 29;560(1):56-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.01.019. Epub 2007 Jan 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17316605 Free PMC article.
-
Duality in response of intracranial vessels to nitroglycerin revealed in rats by imaging photoplethysmography.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 24;13(1):11928. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-39171-w. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37488233 Free PMC article.
-
Acute psilocybin increased cortical activities in rats.Front Neurosci. 2023 May 23;17:1168911. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1168911. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37287797 Free PMC article.
-
Serotonergic regulation of cortical neurovascular coupling and hemodynamics upon awakening from sleep in mice.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024 Sep;44(9):1591-1607. doi: 10.1177/0271678X241238843. Epub 2024 Mar 13. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2024. PMID: 38477254 Free PMC article.
-
Headaches related to triptans therapy in patients of migrainous vertigo.J Headache Pain. 2008 Jun;9(3):185-8. doi: 10.1007/s10194-008-0035-9. Epub 2008 Apr 22. J Headache Pain. 2008. PMID: 18427727 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AUER L.M., LEBER K., SAYAMA I. Effect of serotonin and its antagonist ketanserin on pial vessels. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1985;5:517–522. - PubMed
-
- BOUCHELET I., COHEN Z., CASE B., SEGUELA P., HAMEL E. Multiple microvascular and astroglial 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor subtypes in human brain: molecular and pharmacologic characterization. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1996;19:908–917. - PubMed
-
- COCKS T.M., ANGUS J.A. Endothelium-dependent relaxation of coronary arteries by noradrenaline and serotonin. Nature. 1983;305:627–630. - PubMed
-
- COHEN R.A., SHEPHERD J.T., VANHOUTTE P.M. 5-Hydroxytryptamine can mediate endothelium-dependent relaxation of coronary arteries. Am. J. Physiol. 1983;245:H1077–H1080. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

