Pharmacological block of the slow component of the outward delayed rectifier current (I(Ks)) fails to lengthen rabbit ventricular muscle QT(c) and action potential duration
- PMID: 11156566
- PMCID: PMC1572535
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703777
Pharmacological block of the slow component of the outward delayed rectifier current (I(Ks)) fails to lengthen rabbit ventricular muscle QT(c) and action potential duration
Abstract
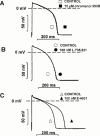
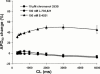
1. The effects of I(Ks) block by chromanol 293B and L-735,821 on rabbit QT-interval, action potential duration (APD), and membrane current were compared to those of E-4031, a recognized I(Kr) blocker. Measurements were made in rabbit Langendorff-perfused whole hearts, isolated papillary muscle, and single isolated ventricular myocytes. 2. Neither chromanol 293B (10 microM) nor L-735,821 (100 nM) had a significant effect on QTc interval in Langendorff-perfused hearts. E-4031 (100 nM), on the other hand, significantly increased QTc interval (35.6+/-3.9%, n=8, P<0.05). 3. Similarly both chromanol 293B (10 microM) and L-735,821 (100 nM) produced little increase in papillary muscle APD (less than 7%) while pacing at cycle lengths between 300 and 5000 ms. In contrast, E-4031 (100 nM) markedly increased (30 - 60%) APD in a reverse frequency-dependent manner. 4. In ventricular myocytes, the same concentrations of chromanol 293B (10 microM), L-735,821 (100 nM) and E-4031 (1 microM) markedly or totally blocked I(Ks) and I(Kr), respectively. 5. I(Ks) tail currents activated slowly (at +30 mV, tau=888.1+/-48.2 ms, n=21) and deactivated rapidly (at -40 mV, tau=157.1+/-4.7 ms, n=22), while I(Kr) tail currents activated rapidly (at +30 mV, tau=35.5+/-3.1 ms, n=26) and deactivated slowly (at -40 mV, tau(1)=641.5+/-29.0 ms, tau(2)=6531+/-343, n=35). I(Kr) was estimated to contribute substantially more to total current density during normal ventricular muscle action potentials (i.e., after a 150 ms square pulse to +30 mV) than does I(Ks). 6. These findings indicate that block of I(Ks) is not likely to provide antiarrhythmic benefit by lengthening normal ventricular muscle QTc, APD, and refractoriness over a wide range of frequencies.
Figures


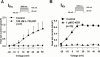


References
-
- ANYUKHOVSKY E.P., SOSUNOV E.U., GAINULLIN R.Z., ROSEN M.R. The controversial M cell. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 1999;10:244–260. - PubMed
-
- BENNET P.B., BEGENISCH T.B. Catecholamines modulate the delayed rectifying potassium current (IK) in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Pflugers Archiv-Eur. J. Physiol. 1987;410:212–219. - PubMed
-
- BILLMAN G.E., HOULE M.S., LYNCH J.J. Selective IKs blockade protects against ventricular fibrillation induced by myocardial ischaemia. Eur Heart J. 1998a;19 Abs. Suppl.:17.
-
- BILLMAN G.E., HOULE M.S., LYNCH J.J. Selective IKs but not IKr blockade protects against ventricular fibrillation induced by myocardial ischaemia. Circulation. 1998b;98:1–52. - PubMed
-
- BOSCH R.F., GASPO R., BUSCH A.E., LANG H.J., LI G.R., NATTEL S. Effects of the chromanol 293B, a selective blocker of the slow component of the delayed rectifier K+ current on repolarization in human and guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Cardiovasc Res. 1998;38:441–450. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

