Modulation of cell adhesion and viability of cultured murine bone marrow cells by arsenobetaine, a major organic arsenic compound in marine animals
- PMID: 11156571
- PMCID: PMC1572548
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703790
Modulation of cell adhesion and viability of cultured murine bone marrow cells by arsenobetaine, a major organic arsenic compound in marine animals
Abstract
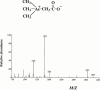
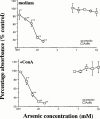
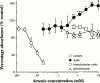
1. In this study, we investigated the biological effects of trimethyl (carboxymethyl) arsonium zwitterion, namely arsenobetaine (AsBe), which is a major organic arsenic compound in marine animals using murine bone marrow (BM) cells and compared them with those of an inorganic arsenical, sodium arsenite, in vitro. 2. Sodium arsenite showed strong cytotoxicity in BM cells, and its IC(50) was 6 microM. In contrast, AsBe significantly enhanced the viability of BM cells in a dose-dependent manner during a 72-h incubation; about a twofold increase in the viability of cells compared with that of control cells cultured with the medium alone was observed with a microM level of AsBe. 3. In morphological investigations, AsBe enhanced the numbers of large mature adherent cells, especially granulocytes, during a 72-h BM culture. When BM cells were cultured together with AsBe and a low dose (1 u ml(-1)) of recombinant murine granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor (rMu GM-CSF), significant additive-like increasing effects were observed on the numbers of both granulocytes and macrophages originated from BM cells. However, AsBe did not cause proliferation of BM cells at all as determined by colony-forming assay using a gelatinous medium. 4. These findings demonstrate the unique and potent biological effects in mammalian cells of AsBe, a major organic arsenic compound in various marine animals which are ingested daily as seafood in many countries.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Stimulation of granulopoiesis by transforming growth factor beta: synergy with granulocyte/macrophage-colony-stimulating factor.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7190-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7190. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991. PMID: 1831268 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of interleukin-4 on the growth of granulocyte-macrophage progenitor cells stimulated by hematopoietic growth factors.J UOEH. 1990 Jun 1;12(2):163-74. doi: 10.7888/juoeh.12.163. J UOEH. 1990. PMID: 1697091
-
Comparison of megakaryopoiesis in vitro of paired peripheral blood progenitor cells and bone marrow harvested during remission in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia.Br J Haematol. 2001 Dec;115(3):563-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2001.03162.x. Br J Haematol. 2001. PMID: 11736936
-
Effect of recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor on murine thrombocytopoiesis in vitro and in vivo.Blood. 1990 Apr 1;75(7):1433-8. Blood. 1990. PMID: 2180495
-
Culture of ovine bone marrow-derived macrophages and evidence for serum factors distinct from M-CSF contributing to their propagation in vitro.J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Jun;51(6):525-34. doi: 10.1002/jlb.51.6.525. J Leukoc Biol. 1992. PMID: 1613390
References
-
- AHMED S.A., GOGAL R.M., JR, WALSH J.E. A new rapid and simple non-radioactive assay to monitor and determine the proliferation of lymphocytes: An alternative to H3-thymidine incorporation assay. J. Immunol. Methods. 1994;170:211–224. - PubMed
-
- BUCHET J.P., LAUWERYS R., ROELS H. Comparison of several methods for the determination of arsenic compounds in water and in urine. Their applications for the study of arsenic metabolism and for the monitoring of workers exposed to arsenic. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health. 1980;46:11–29. - PubMed
-
- CANNON J.R., EDMONDS J.S., FRANCESCONI K.A., RASTON C.L., SAUNDERS J.B., SKELTON B.W., WHITE A.H. Isolation, crystal structure and synthesis of arsenobetaine, a constituent of the western rock lobster, the dusky shark, and some samples of human urine. Aust. J. Chem. 1981;34:787–798.
-
- CHEN G.-Q., SHI X.-G., TANG W., XIONG S.-M., ZHU J., CAI X., HAN Z.-G., NI J.-H., SHI G.-Y., JIA P.-M., LIU M.-M., HE K.-L., NIU C., MA J., ZHANG P., ZHANG T.-D., PAUL P., NAOE T., KITAMURA K., MILLER W., WAXMAN S., WANG Z.-Y., DE THE H., CHEN S.-J., CHEN Z. Use of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): I .As2O3 exerts dose-dependent dual effects on APL cells. Blood. 1997;89:3345–3353. - PubMed
-
- EDMONDS J.S., FRANCESCONI K.A. Arseno-sugars from brown kelp (Ecklonia radista) as intermediates in cycling of arsenic in marine ecosystem. Nature (London) 1981;289:602–604.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

