Contralateral but not systemic administration of the kappa-opioid agonist U-50,488H induces anti-nociception in acute hindpaw inflammation in rats
- PMID: 11156584
- PMCID: PMC1572540
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703782
Contralateral but not systemic administration of the kappa-opioid agonist U-50,488H induces anti-nociception in acute hindpaw inflammation in rats
Abstract
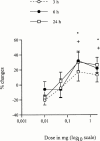
1. The anti-nociceptive effects of contralateral administration of kappa-opioid agonist U-50,488H were investigated in rats. 2. Inflammation was induced by unilateral injection of 1% carrageenan into the right hindpaw. Prior to carrageenan injection, U-50,488H or saline was administered into the left hindpaw. Withdrawal responses to mechanical and heat stimulation and oedema levels were evaluated at 3, 6 and 24 h post-carrageenan injection. 3. The results showed that the inflammatory effect of 1% carrageenan peaked after 6 h with bilateral decreases in withdrawal latencies and ipsilateral oedema formation. 4. Contralateral treatment with 0.01, 0.05, 0.3 and 2 mg of U-50,488H attenuated nociceptive reflexes to mechanical stimulation on the inflamed side at 6 h. The anti-nociceptive effect of contralateral treatment was dose-dependent at 3 and 24 h. The hindpaw withdrawal latencies to heat stimulation were prolonged at 3 and 24 h after contralateral treatment with 0.3 mg U-50,488H. No effect on inflammatory oedema formation was observed, except for a decrease at 3 h after treatment with 2 mg of U-50,488H. 5. Sciatic nerve denervation on the contralateral side abolished the anti-nociceptive effects of U-50,488H (0.3 and 2 mg). In contrast, contralateral injection of 1 mg morphine prolonged paw latencies in denervated rats. 6. Both co-administration of the peripherally selective opioid antagonist naloxone methiodide with 0.3 mg U-50,488H, and alternatively, systemic administration of 0.3 mg U-50,488H reversed the anti-nociceptive effects induced by contralateral injection of U-50,488H. 7. Taken together, our findings indicate that the contralateral administration of U-50,488H attenuates nociceptive behaviour resulting from acute inflammation. The effect is mediated via peripheral neuronal kappa-opioid receptors and, possibly, spinal cord mechanisms, suggesting a new treatment approach for acute inflammatory conditions.
Figures

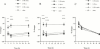
Similar articles
-
Contralateral, ipsilateral and bilateral treatments with the kappa-opioid receptor agonist U-50,488H in mononeuropathic rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2004 Jun 28;494(2-3):139-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.04.043. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15212967
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of contralateral administration of the kappa-opioid agonist U-50,488H in rats with unilaterally induced adjuvant arthritis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006 Mar;45(3):295-302. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kei156. Epub 2005 Oct 25. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2006. PMID: 16249243
-
The site of anti-arthritic action of the kappa-opioid, U-50, 488H, in adjuvant arthritis: importance of local administration.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Aug;118(7):1754-60. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15601.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8842441 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of kappa-opioid receptor agonists in learning and memory impairment in animal models.Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1998 Sep;20(7):595-9. doi: 10.1358/mf.1998.20.7.485724. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9819804 Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory effects of opioids.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003;521:148-60. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2003. PMID: 12617572 Review.
Cited by
-
Opioid Analgesia and Opioid-Induced Adverse Effects: A Review.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Oct 27;14(11):1091. doi: 10.3390/ph14111091. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34832873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post heat shock tolerance: a neuroimmunological anti-inflammatory phenomenon.J Inflamm (Lond). 2009 Mar 27;6:7. doi: 10.1186/1476-9255-6-7. J Inflamm (Lond). 2009. PMID: 19327140 Free PMC article.
-
Antinociceptive Effects of Kappa-Opioid Receptor Agonists.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022;271:293-313. doi: 10.1007/164_2020_430. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 33387069 Review.
-
Mu-opioid receptor in the nucleus submedius: involvement in opioid-induced inhibition of mirror-image allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain.Neurochem Res. 2008 Oct;33(10):2134-41. doi: 10.1007/s11064-008-9733-6. Epub 2008 May 13. Neurochem Res. 2008. PMID: 18473169
References
-
- BARTHO L., SZOLCSANYI J. Opiate agonists inhibit neurogenic plasma extravasation in the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1981;73:101–104. - PubMed
-
- BILEVICIUTE-LJUNGAR I., LUNDEBERG T. Contralateral but not systemic administration of bupivacaine reduces acute inflammation in the rat hindpaw. Somatosens. Motor. Res. 2000a;17:285–293. - PubMed
-
- BILEVICIUTE-LJUNGAR I., LUNDEBERG T. Contralateral treatment with xylocaine reduces nociceptive behaviour in mononeuropathic rats. NeuroReport. 2000b;11:291–295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

