Endotoxin sensitization to kinin B(1) receptor agonist in a non-human primate model: haemodynamic and pro-inflammatory effects
- PMID: 11156593
- PMCID: PMC1572522
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703748
Endotoxin sensitization to kinin B(1) receptor agonist in a non-human primate model: haemodynamic and pro-inflammatory effects
Abstract
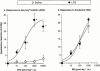
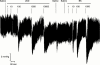
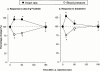
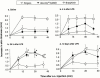
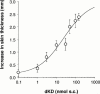
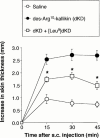
1. Although endotoxaemia induces kinin B(1) receptors in several animal models, this condition is not documented in primates. This study examined the up-regulation of haemodynamic and pro-inflammatory responses to the B(1) agonist des-Arg(10)-kallidin (dKD) in a non-human primate model. 2. Green monkeys (Cercopithecus aethiops St Kitts) received lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 90 microg kg(-1)) or saline intravenously. After 4 h, anaesthetized monkeys were cannulated via the carotid artery to monitor blood pressure changes following intra-arterial injections of dKD or the B(2) agonist bradykinin (BK). Oedema induced by subcutaneous kinin administration was evaluated as the increase in ventral skin folds in anaesthetized monkeys injected with captopril at 4 h to 56 days post-LPS. 3. LPS increased rectal temperature but did not affect blood pressure after 4 h. dKD reduced blood pressure (E(max): 27+/-4 mmHg; EC(50): 130 pmol kg(-1)) and increased heart rate (E(max): 33 b.p.m.) only after LPS. In contrast, the dose-dependent fall in blood pressure with BK was comparable in all groups. The selective B(1) antagonist [Leu(9)]dKD (75 ng kg(-1) min(-1), intravenously) abolished responses to dKD but not BK. 4. dKD injection induced oedema dose-dependently (2.4+/-0.1 mm at 150 nmol) only following LPS (at 4 h to 12 days but not 56 days). In contrast, BK-induced oedema was present and stable in all monkeys. Co-administration of [Leu(9)]dKD (150 nmol) significantly reduced oedema induced by dKD (50 nmol). 5. These results suggest LPS up-regulation of B(1) receptor effects in green monkeys. This non-human primate model may be suitable for testing new, selective B(1) antagonists with therapeutic potential as anti-inflammatory agents.
Figures
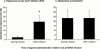
Similar articles
-
Characterization of the receptor and the mechanisms underlying the inflammatory response induced by des-Arg9-BK in mouse pleurisy.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Jan;123(2):281-91. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701590. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9489617 Free PMC article.
-
The role of B1 and B2 kinin receptors in oedema formation after long-term treatment with Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG).Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Feb;120(3):502-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0700914. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9031756 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatment with Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) potentiates kinin B1 receptor agonist-induced nociception and oedema formation in the formalin test in mice.Neuropeptides. 1998 Oct;32(5):393-403. doi: 10.1016/s0143-4179(98)90062-2. Neuropeptides. 1998. PMID: 9844998
-
Upregulation of B1 receptor mediating des-Arg9-BK-induced rat paw oedema by systemic treatment with bacterial endotoxin.Br J Pharmacol. 1996 Mar;117(5):793-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1996.tb15262.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8851492 Free PMC article.
-
The role of sensorial neuropeptides in the edematogenic responses mediated by B(1) agonist des-Arg(9)-BK in rats pre-treated with LPS.Regul Pept. 2000 May 10;89(1-3):29-35. doi: 10.1016/s0167-0115(00)00094-x. Regul Pept. 2000. PMID: 10771310
Cited by
-
Activation of TRPV1 by capsaicin induces functional kinin B(1) receptor in rat spinal cord microglia.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Jan 20;9:16. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-16. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22264228 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of ligand-induced regulation of kinin receptor expression in the rabbit.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Aug;133(7):1154-62. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704158. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11487527 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Bradykinin Receptors in Hereditary Angioedema Due to C1-Inhibitor Deficiency.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 7;23(18):10332. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810332. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142237 Free PMC article.
-
The kinin B1 receptor antagonist SSR240612 reverses tactile and cold allodynia in an experimental rat model of insulin resistance.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Sep;152(2):280-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707388. Epub 2007 Jul 9. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17618300 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the genes encoding kinin receptors are increased in human carotid atherosclerotic plaques.Biomed Rep. 2015 May;3(3):398-402. doi: 10.3892/br.2015.421. Epub 2015 Jan 29. Biomed Rep. 2015. PMID: 26137244 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AHLUWALIA A., PERRETTI M. B1 receptors as a new inflammatory target. Could this B the 1. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 1999;20:100–104. - PubMed
-
- ALTAMURA M., MEINI S., QUARTARA L., MAGGI C.A. Nonpeptide antagonists for kinin receptors. Regul. Pept. 1999;80:13–26. - PubMed
-
- AUDET R., PETITCLERC E., DRAPEAU G., RIOUX F., MARCEAU F. Further analysis of the upregulation of bradykinin B1 receptors in isolated rabbit aorta by using metabolic inhibitors. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 1994;271:551–555. - PubMed
-
- AUDET R., RIOUX F., DRAPEAU G., MARCEAU F. Cardiovascular effects of Sar-[D-Phe8]des-Arg9-bradykinin, a metabolically protected agonist of B1 receptor for kinins, in the anesthetized rabbit pretreated with a sublethal dose of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997;280:6–15. - PubMed
-
- BASTIAN S., PAQUET J.L., ROBERT C., CREMERS B., LOILLIER B., LARRIVEE J.F., BACHVAROV D.R., MARCEAU F., PRUNEAU D. Interleukin 8 (IL-8) induces the expression of kinin B1 receptor in human lung fibroblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998;253:750–755. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

