High-throughput SNP genotyping by allele-specific PCR with universal energy-transfer-labeled primers
- PMID: 11156625
- PMCID: PMC311033
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.157901
High-throughput SNP genotyping by allele-specific PCR with universal energy-transfer-labeled primers
Abstract
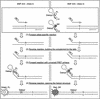
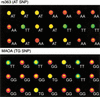
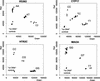
We have developed a new method for high-throughput genotyping of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The technique involves PCR amplification of genomic DNA with two tailed allele-specific primers that introduce priming sites for universal energy-transfer-labeled primers. The output of red and green light is conveniently scored using a fluorescence plate reader. The new method, which was validated on nine model SNPs, is well suited for high-throughput, automated genotyping because it requires only one reaction per SNP, it is performed in a single tube with no post-PCR handling, the same energy-transfer-labeled primers are used for all analyses, and the instrumentation is inexpensive. Possible applications include multiple-candidate gene analysis, genomewide scans, and medical diagnostics.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A multiplex SNP genotyping by allele-specificspecific PCR based on stem-loop and universal fluorescent primers of Chr1daxin mice.Electrophoresis. 2019 Jun;40(11):1600-1605. doi: 10.1002/elps.201900052. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Electrophoresis. 2019. PMID: 30801725
-
Miniaturized sealed-tube allele-specific PCR.Hum Mutat. 2002 May;19(5):543-53. doi: 10.1002/humu.10060. Hum Mutat. 2002. PMID: 11968087
-
A high-throughput SNP typing system for genome-wide association studies.J Hum Genet. 2001;46(8):471-7. doi: 10.1007/s100380170047. J Hum Genet. 2001. PMID: 11501945
-
High-throughput genotyping with energy transfer-labeled primers.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;335:215-40. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-069-3:215. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16785631 Review.
-
Multiplex genotyping for thrombophilia-associated SNPs by universal bead arrays.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;496:59-72. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-553-4_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 18839105 Review.
Cited by
-
One-Step ARMS-PCR for the Detection of SNPs-Using the Example of the PADI4 Gene.Methods Protoc. 2019 Jul 25;2(3):63. doi: 10.3390/mps2030063. Methods Protoc. 2019. PMID: 31349745 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of genetics risk score and fatty acids quality indices on healthy and unhealthy obesity phenotype.BMC Med Genomics. 2025 Jan 21;18(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-02066-4. BMC Med Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39838481 Free PMC article.
-
Association study in the 5q31-32 linkage region for schizophrenia using pooled DNA genotyping.BMC Psychiatry. 2008 Feb 25;8:11. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-8-11. BMC Psychiatry. 2008. PMID: 18298822 Free PMC article.
-
Promoter polymorphisms in ACE (angiotensin I-converting enzyme) associated with clinical outcomes in hypertension.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2009 Jan;85(1):36-44. doi: 10.1038/clpt.2008.194. Epub 2008 Oct 22. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2009. PMID: 18946466 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic studies of quantitative MCI and AD phenotypes in ADNI: Progress, opportunities, and plans.Alzheimers Dement. 2015 Jul;11(7):792-814. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2015.05.009. Alzheimers Dement. 2015. PMID: 26194313 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baron H, Fung S, Aydin A, Bahring S, Luft FC, Schuster H. Oligonucleotide ligation assay (OLA) for the diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia. Nat Biotechnol. 1996;14:1279–1282. - PubMed
-
- Blomeke B, Sieben S, Spotter D, Landt O, Merk HF. Identification of N-acetyltransferase 2 genotypes by continuous monitoring of fluorogenic hybridization probes. Anal Biochem. 1999;275:93–97. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
