Importance of rate control or rate regulation for improving exercise capacity and quality of life in patients with permanent atrial fibrillation and normal left ventricular function: a randomised controlled study
- PMID: 11156667
- PMCID: PMC1729623
- DOI: 10.1136/heart.85.2.171
Importance of rate control or rate regulation for improving exercise capacity and quality of life in patients with permanent atrial fibrillation and normal left ventricular function: a randomised controlled study
Abstract
Objective: To determine the importance of rhythm regulation or rate control in patients with permanent atrial fibrillation (AF) and normal left ventricular function.
Patients and interventions: Thirty six patients with a mixed fast and slow ventricular response rate to their AF were randomised to either His bundle ablation (HBA) and VVIR pacemaker (HBA group) or VVI pacemaker and atrioventricular modifying drugs (Med group). Outcomes assessed at one, three, six, and 12 months included exercise duration and quality of life.
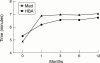
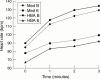
Results: Exercise duration significantly improved from baseline in both groups. There was no difference in outcome between the groups (Med +40% v HBA +20%, p = NS). The heart rate profile on exercise was similarly slowed in both groups compared to baseline. Quality of life significantly improved in both treatment arms for the modified Karolinska questionnaire (KQ) (Med +50% v HBA +50%, p = NS) and the Nottingham health profile (NHP) (Med +40% v HBA +20%, p = NS). However, for the individual symptom scores of each questionnaire more were improved in the Med group (KQ-Med 6 improved v HBA 4, NHP-Med 3 v HBA 1). Left ventricular function was equally preserved by both treatments during follow up.
Conclusion: In these patients control of ventricular response rate with either HBA + VVIR pacemaker or atrioventricular modifying drugs + VVI pacemaker will lead to a significant improvement in exercise duration and quality of life. Rhythm regulation by HBA did not confer additional benefit, suggesting rate control alone is necessary for the successful symptomatic treatment of these patients in permanent AF.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Ablate and Pace Trial: a prospective study of catheter ablation of the AV conduction system and permanent pacemaker implantation for treatment of atrial fibrillation. APT Investigators.J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 1998 Jun;2(2):121-35. doi: 10.1023/a:1009795330454. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 1998. PMID: 9870004
-
The Australian Intervention Randomized Control of Rate in Atrial Fibrillation Trial (AIRCRAFT).J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003 May 21;41(10):1697-702. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(03)00338-3. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2003. PMID: 12767649 Clinical Trial.
-
[Left ventricular systolic function, paced QT dispersion, exercise tolerance and quality of life in long term follow up after ventricular pacemaker implantation (VVIR) and radiofrequency atrioventricular junction ablation in drug refractory atrial fibrillation].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2008 Mar;24(141):190-4. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2008. PMID: 18634282 Polish.
-
Catheter Ablation Versus Medical Therapy for Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With Heart Failure: A Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials.Heart Lung Circ. 2019 May;28(5):707-718. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2018.10.022. Epub 2018 Nov 17. Heart Lung Circ. 2019. PMID: 30509786 Review.
-
Comparison of permanent left ventricular and biventricular pacing in patients with heart failure and chronic atrial fibrillation: a prospective hemodynamic study.Card Electrophysiol Rev. 2003 Dec;7(4):315-24. doi: 10.1023/B:CEPR.0000023167.11038.8f. Card Electrophysiol Rev. 2003. PMID: 15071245 Review.
Cited by
-
Kinetics of left ventricular rotation during exercise and its relation to exercise tolerance in atrial fibrillation: assessment by two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography.J Echocardiogr. 2014 Sep;12(3):89-97. doi: 10.1007/s12574-014-0205-5. Epub 2014 Feb 11. J Echocardiogr. 2014. PMID: 27276892
-
The state of patient-reported outcomes in atrial fibrillation : a review of current measures.Pharmacoeconomics. 2005;23(7):687-708. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200523070-00004. Pharmacoeconomics. 2005. PMID: 15987226 Review.
-
Adverse effects of continuous ventricular pacing in patients with slower atrial fibrillation and normal left ventricular systolic function.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2008 Apr;13(2):130-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1542-474X.2008.00212.x. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2008. PMID: 18426438 Free PMC article.
-
CHA2DS2-VASc score predicts exercise intolerance in young and middle-aged male patients with asymptomatic atrial fibrillation.Sci Rep. 2018 Dec 21;8(1):18039. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36185-7. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30575764 Free PMC article.
-
A common β1-adrenergic receptor polymorphism predicts favorable response to rate-control therapy in atrial fibrillation.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012 Jan 3;59(1):49-56. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.08.061. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22192668 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
