Volumetric analysis of the germinal matrix and lateral ventricles performed using MR images of postmortem fetuses
- PMID: 11156787
- PMCID: PMC7973932
Volumetric analysis of the germinal matrix and lateral ventricles performed using MR images of postmortem fetuses
Abstract
Background and purpose: The volumetric changes of the ventricular system and germinal matrix are important to understand brain maturation and the mechanism of subependymal hemorrhage. Our purpose was to show the 3D configuration of the brain, germinal matrix, and lateral ventricles and to discuss the volumetric changes of each structure with maturation by using high-resolution MR imaging.
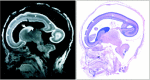
Methods: Three-dimensional MR images of 13 formalin-fixed fetal brains ranging from 7 to 28 weeks' gestational age (GA) were obtained on a 4.7-T unit. Each 3D configuration of the brain surface, germinal matrix, and ventricles was rendered from the cross-sectional imaging data sets and its volume measured.
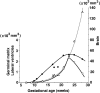
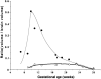
Results: The germinal matrix was detected on MR images at 9 weeks' GA. Its volume exponentially increased by 23 weeks' GA (maximum, 2346 mm3) and then sharply decreased at 28 weeks' GA. The volume of the lateral ventricles increased gradually and reached 2646 mm3 peak volume at 23 weeks' GA. Between 11 and 23 weeks' GA, total brain and germinal matrix volumes were exponentially increasing, but the volume ratio of germinal matrix to brain was stable at about 5%. On the other hand, the volume ratio of lateral ventricles to brain was large between 10 and 13 weeks' GA. This period corresponded to the lateral ventricle showing a "vesicular" aspect with a thin mantle, and the developing mantle thickness of the hemisphere resulted in the decreasing ratio.
Conclusion: Volumetric information concerning the germinal matrix and lateral ventricles may be useful in the accurate interpretation of clinical echograms and MR images of the fetal brain in utero.
Figures




References
-
- McGahan JP, Phillips HE. Ultrasonic evaluation of the size of the trigone of the fetal ventricle. J Ultrasound Med 1983;2:315-319 - PubMed
-
- Pasto ME, Kurtz AB. Ultrasonography of the normal fetal brain. Neuroradiology 1986;28:380-385 - PubMed
-
- Pilu G, De PL, Romero R, Bovicelli L, Hobbins JC. The fetal subarachnoid cisterns: an ultrasound study with report of a case of congenital communicating hydrocephalus. J Ultrasound Med 1986;5:365-372 - PubMed
-
- Yagel S, Palti Z, Hurwitz A. Detailed sonographic mappings of normal fetal brain anatomy in utero at six levels in the axial plain. Am J Perinatol 1985;2:134-137 - PubMed
-
- Johnson IR, Stehling MK, Blamire AM, et al. Study of internal structure of the human fetus in utero by echo-planar magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1990;163:601-607 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
