Impairment of CD4(+) T cell responses during chronic virus infection prevents neutralizing antibody responses against virus escape mutants
- PMID: 11157050
- PMCID: PMC2195917
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.193.3.297
Impairment of CD4(+) T cell responses during chronic virus infection prevents neutralizing antibody responses against virus escape mutants
Abstract
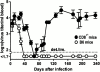
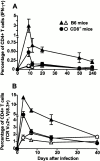
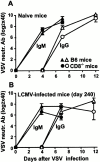
We have shown previously that neutralizing antibodies (nAbs) are important contributors to the long-term immune control of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection, particularly if cytotoxic T cell responses are low or absent. Nevertheless, virus escape from the nAb response due to mutations within the surface glycoprotein gene may subsequently allow the virus to persist. Here we show that most of the antibody-escape viral mutants retain their immunogenicity. We present evidence that the failure of the infected host to mount effective humoral responses against emerging neutralization-escape mutants correlates with the rapid loss of CD4(+) T cell responsiveness during the establishment of viral persistence. Similar mechanisms may contribute to the persistence of some human pathogens such as hepatitis B and C viruses, and human immunodeficiency virus.
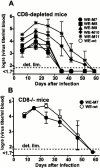
Figures

References
-
- Kagi D., Ledermann B., Bürki K., Seiler P., Odermatt B., Olsen K.J., Podack E.R., Zinkernagel R.M., Hengartner H. Cytotoxicity mediated by T cells and natural killer cells is greatly impaired in perforin-deficient mice. Nature. 1994;369:31–37. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz J.E., Kuroda M.J., Santra S., Sasseville V.G., Simon M.A., Lifton M.A., Racz P., Tenner-Racz K., Dalesandro M., Scallon B.J. Control of viremia in simian immunodeficiency virus infection by CD8+ lymphocytes. Science. 1999;283:857–860. - PubMed
-
- Planz O., Ehl S., Furrer E., Horvath E., Brundler M.A., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R.M. A critical role for neutralizing-antibody-producing B cells, CD4+ T cells, and interferons in persistent and acute infections of mice with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virusimplications for adoptive immunotherapy of virus carriers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1997;94:6874–6879. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Thomsen A.R., Johansen J., Marker O., Christensen J.P. Exhaustion of CTL memory and recrudescence of viremia in lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-infected MHC class II- deficient mice and B cell- deficient mice. J. Immunol. 1996;157:3074–3080. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

