CD4(+) T cells from lupus-prone mice are hyperresponsive to T cell receptor engagement with low and high affinity peptide antigens: a model to explain spontaneous T cell activation in lupus
- PMID: 11157053
- PMCID: PMC2195926
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.193.3.329
CD4(+) T cells from lupus-prone mice are hyperresponsive to T cell receptor engagement with low and high affinity peptide antigens: a model to explain spontaneous T cell activation in lupus
Abstract
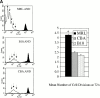
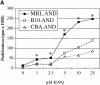
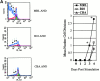
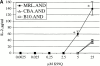
Polyclonal CD4(+) T cell activation is characteristic of spontaneous lupus. As a potential explanation for this phenotype, we hypothesized that T cells from lupus-prone mice are intrinsically hyperresponsive to stimulation with antigen, particularly to those peptide ligands having a low affinity for the T cell receptor (TCR). To test this hypothesis, we backcrossed the alpha and beta chain genes of the AND TCR specific for amino acids 88-104 of pigeon cytochrome C (PCC) to the Fas-intact MRL/Mp(+)(Fas-lpr) and to the H-2(k)-matched control backgrounds B10.BR and CBA/CaJ (MRL.AND, B10.AND, and CBA.AND, respectively), and assessed naive CD4(+) TCR transgenic T cell activation in vitro after its encounter with cognate antigen and lower affinity altered peptide ligands (APLs). MRL.AND T cells, compared with control B10.AND and CBA.AND cells, proliferated more when stimulated with agonist antigen. More strikingly, MRL.AND T cells proliferated significantly more and produced more interleukin 2 when stimulated with the APLs of PCC 88-104, having lower affinity for the transgenic TCR. These results imply that one of the forces driving polyclonal activation of alpha/beta T cells in lupus is an intrinsically heightened response to peptide antigen, particularly those with low affinity for the TCR, independent of the nature of the antigen-presenting cell and degree of costimulation.
Figures







References
-
- Wofsy D., Ledbetter J.A., Hendler P.L., Seaman W.E. Treatment of murine lupus with monoclonal anti-T cell antibody. J. Immunol. 1985;134:852–857. - PubMed
-
- Peng S.L., Madaio M.P., Hughes D.P., Crispe I.N., Owen M.J., Wen L., Hayday A.C., Craft J. Murine lupus in the absence of αβ T cells. J. Immunol. 1996;156:4041–4049. - PubMed
-
- Rozzo S.J., Drake C.G., Chiang B.L., Gershwin M.E., Kotzin B.L. Evidence for polyclonal T cell activation in murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Immunol. 1994;153:1340–1351. - PubMed
-
- Fatenejad S., Peng S.L., Disorbo O., Craft J. Central T cell tolerance in lupus-prone miceinfluence of autoimmune background and the lpr mutation. J. Immunol. 1998;161:6427–6432. - PubMed
-
- Sloan-Lancaster J., Allen P.M. Altered peptide ligand-induced partial T cell activationmolecular mechanisms and role in T cell biology. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996;14:1–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

