Two distal downstream enhancers direct expression of the human apolipoprotein E gene to astrocytes in the brain
- PMID: 11157067
- PMCID: PMC6762321
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-03-00812.2001
Two distal downstream enhancers direct expression of the human apolipoprotein E gene to astrocytes in the brain
Abstract
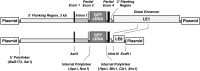
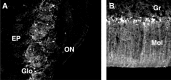
Two distal downstream enhancers controlling astrocyte expression of the human apolipoprotein E (apoE) gene in the brain were identified by analysis of transgenic mice generated with various constructs of the apoE/C-I/C-IV/C-II gene cluster. In wild-type mice, the highest overall levels of apoE mRNA were found in astrocytes in the glomerular layer of olfactory bulbs and in Bergmann glia in the cerebellum. This pattern of expression was reproduced in transgenic mice expressing the entire human apoE gene cluster and also in transgenic mice expressing specific enhancer segments within the cluster. Expression of the human apoE transgene at these sites was specified by two enhancer domains: one enhancer is located 3.3 kb downstream of the apoE gene, and a duplication of this sequence is located 15 kb downstream of the apoE gene. Astrocyte enhancer activity was contained within 620 and 619 bp segments of these domains that show subtle differences in regional expression. In the absence of these distal enhancers, the apoE gene was not expressed in astrocytes. The relatively high levels of apoE expression at specific sites in the olfactory bulb and cerebellum suggest the presence of unique regulatory signals at these locations that may reflect common cellular properties and apoE gene functions. The localization of the two astrocytic enhancers reveals an unexpected complexity in the control of apoE production that is essential to understanding apoE function in the brain.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Duplicated downstream enhancers control expression of the human apolipoprotein E gene in macrophages and adipose tissue.J Biol Chem. 2000 Oct 13;275(41):31567-72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005468200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10893248
-
A far-downstream hepatocyte-specific control region directs expression of the linked human apolipoprotein E and C-I genes in transgenic mice.J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8221-9. J Biol Chem. 1993. PMID: 7681840
-
Expression of the apolipoprotein E gene in the skin is controlled by a unique downstream enhancer.J Invest Dermatol. 2001 Jan;116(1):77-84. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2001.00213.x. J Invest Dermatol. 2001. PMID: 11168801
-
Transcriptional regulation of the human apolipoprotein genes.Front Biosci. 2001 Mar 1;6:D456-504. doi: 10.2741/zannis. Front Biosci. 2001. PMID: 11229886 Review.
-
Apolipoprotein E as a target for developing new therapeutics for Alzheimer's disease based on studies from protein, RNA, and regulatory region of the gene.J Mol Neurosci. 2004;23(3):225-33. doi: 10.1385/JMN:23:3:225. J Mol Neurosci. 2004. PMID: 15181251 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs in brain cholesterol metabolism and their implications for Alzheimer's disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Dec;1861(12 Pt B):2139-2147. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.04.020. Epub 2016 May 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 27155217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synapses, Microglia, and Lipids in Alzheimer's Disease.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jan 12;15:778822. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.778822. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35095394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of genetic polymorphisms on Alzheimer's disease treatment outcomes: an update.Clin Interv Aging. 2019 Mar 29;14:631-642. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S200109. eCollection 2019. Clin Interv Aging. 2019. PMID: 30992661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A rapid and cost-effective method for genotyping apolipoprotein E gene polymorphism.Mol Neurodegener. 2016 Jan 12;11:2. doi: 10.1186/s13024-016-0069-4. Mol Neurodegener. 2016. PMID: 26754117 Free PMC article.
-
APOE and TREM2 regulate amyloid-responsive microglia in Alzheimer's disease.Acta Neuropathol. 2020 Oct;140(4):477-493. doi: 10.1007/s00401-020-02200-3. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Acta Neuropathol. 2020. PMID: 32840654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allan CM, Walker D, Segrest JP, Taylor JM. Identification and characterization of a new human gene (APOC4) in the apolipoprotein E, C-I, and C-II gene locus. Genomics. 1995a;28:291–300. - PubMed
-
- Allan CM, Walker D, Taylor JM. Evolutionary duplication of a hepatic control region in the human apolipoprotein E gene locus. Identification of a second region that confers high-level and liver-specific expression of the human apolipoprotein E gene in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1995b;270:26278–26281. - PubMed
-
- Allan CM, Taylor S, Taylor JM. Two hepatic enhancers, HCR.1 and HCR.2, coordinate the liver expression of the entire human apolipoprotein E/C-I/C-IV/C-II gene cluster. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:29113–29119. - PubMed
-
- Bacon AW, Bondi MW, Salmon DP, Murphy C. Very early changes in olfactory functioning due to Alzheimer's disease and the role of apolipoprotein E in olfaction. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1998;855:723–731. - PubMed
-
- Bar I, Lambert de Rouvroit C, Royaux I, Krizman DB, Dernoncourt C, Ruelle D, Beckers MC, Goffinet AM. A YAC contig containing the reeler locus with preliminary characterization of candidate gene fragments. Genomics. 1995;26:543–549. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
