GABAb receptors regulate chick retinal calcium waves
- PMID: 11157076
- PMCID: PMC6762318
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-03-00897.2001
GABAb receptors regulate chick retinal calcium waves
Abstract
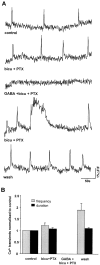
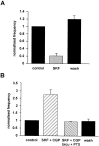
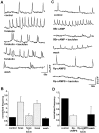
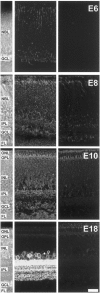
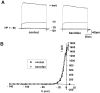
Correlated spiking activity and associated Ca(2+) waves in the developing retina are important in determining the connectivity of the visual system. Here, we show that GABA, via GABA(B) receptors, regulates the temporal characteristics of Ca(2+) waves occurring before synapse formation in the embryonic chick retina. Blocking ionotropic GABA receptors did no affect these Ca(2+) transients. However, when these receptors were blocked, GABA abolished the transients, as did the GABA(B) agonist baclofen. The action of baclofen was prevented by the GABA(B) antagonist p-3-aminopropyl-p-diethoxymethyl phosphoric acid (CGP35348). CGP35348 alone increased the duration of the transients, showing that GABA(B) receptors are tonically activated by endogenous GABA. Blocking the GABA transporter GAT-1 with 1-(4,4-diphenyl-3-butenyl)-3-piperidine carboxylic acid (SKF89976A) reduced the frequency of the transients. This reduction was prevented by CGP35348 and thus resulted from activation of GABA(B) receptors by an increase in external [GABA]. The effect of GABA(B) receptor activation persisted in the presence of activators and blockers of the cAMP-PKA pathway. Immunocytochemistry showed GABA(B) receptors and GAT-1 transporters on ganglion and amacrine cells from the earliest times when Ca(2+) waves occur (embryonic day 8). Patch-clamp recordings showed that K(+) channels on ganglion cell layer neurons are not modulated by GABA(B) receptors, whereas Ca(2+) channels are; however, Ca(2+) channel blockade with omega-conotoxin-GVIA or nimodipine did not prevent Ca(2+) waves. Thus, the regulation of Ca(2+) waves by GABA(B) receptors occurs independently of N- and L-type Ca(2+) channels and does not involve K(+) channels of the ganglion cell layer. GABA(B) receptors are likely to be of key importance in regulating retinal development.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Mu-opioid and GABA(B) receptors modulate different types of Ca2+ currents in rat nodose ganglion neurons.Neuroscience. 1998 Aug;85(3):939-56. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(97)00674-x. Neuroscience. 1998. PMID: 9639286
-
Carrier-mediated GABA release activates GABA receptors on hippocampal neurons.J Neurophysiol. 1998 Jul;80(1):270-81. doi: 10.1152/jn.1998.80.1.270. J Neurophysiol. 1998. PMID: 9658049
-
GABA transporters regulate inhibition in the retina by limiting GABA(C) receptor activation.J Neurosci. 2002 Apr 15;22(8):3285-92. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-08-03285.2002. J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11943830 Free PMC article.
-
International Union of Pharmacology. XXXIII. Mammalian gamma-aminobutyric acid(B) receptors: structure and function.Pharmacol Rev. 2002 Jun;54(2):247-64. doi: 10.1124/pr.54.2.247. Pharmacol Rev. 2002. PMID: 12037141 Review.
-
Regulation of neuronal GABA(B) receptor functions by subunit composition.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012 May 18;13(6):380-94. doi: 10.1038/nrn3249. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22595784 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging neurotrophic role of GABAB receptors in neuronal circuit development.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Nov 12;7:206. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00206. eCollection 2013. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24282395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A critical role of the strychnine-sensitive glycinergic system in spontaneous retinal waves of the developing rabbit.J Neurosci. 2001 Jul 15;21(14):5158-68. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-14-05158.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11438591 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeine exposure ameliorates acute ischemic cell death in avian developing retina.Purinergic Signal. 2020 Mar;16(1):41-59. doi: 10.1007/s11302-020-09687-1. Epub 2020 Feb 20. Purinergic Signal. 2020. PMID: 32078115 Free PMC article.
-
Stage-dependent dynamics and modulation of spontaneous waves in the developing rabbit retina.J Physiol. 2004 Oct 15;560(Pt 2):533-49. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.066597. Epub 2004 Aug 12. J Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15308679 Free PMC article.
-
GABAB receptor antagonist CGP46381 inhibits form-deprivation myopia development in guinea pigs.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:207312. doi: 10.1155/2015/207312. Epub 2015 Jan 11. Biomed Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25649745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bettler B, Kaupmann K, Bowery N. GABAB receptors: drugs meet clones. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1998;8:345–350. - PubMed
-
- Blazynski C. Displaced cholinergic, GABAergic amacrine cells in the rabbit retina also contain adenosine. Vis Neurosci. 1989;3:425–431. - PubMed
-
- Bonness V, Catsicas M, Cunningham J, Hutson P, Murray F, Neal M, Mobbs P. Depolarization-evoked transmitter release and agonist-evoked increases in [Ca2+]i in the early development of the chick retina. J Physiol (Lond) 1996;494:79.P.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
