Dissection of central carbon metabolism of hemoglobin-expressing Escherichia coli by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance flux distribution analysis in microaerobic bioprocesses
- PMID: 11157231
- PMCID: PMC92635
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.67.2.680-687.2001
Dissection of central carbon metabolism of hemoglobin-expressing Escherichia coli by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance flux distribution analysis in microaerobic bioprocesses
Abstract
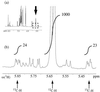
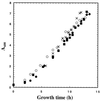
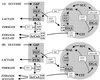
Escherichia coli MG1655 cells expressing Vitreoscilla hemoglobin (VHb), Alcaligenes eutrophus flavohemoprotein (FHP), the N-terminal hemoglobin domain of FHP (FHPg), and a fusion protein which comprises VHb and the A. eutrophus C-terminal reductase domain (VHb-Red) were grown in a microaerobic bioreactor to study the effects of low oxygen concentrations on the central carbon metabolism, using fractional (13)C-labeling of the proteinogenic amino acids and two-dimensional [(13)C, (1)H]-correlation nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The NMR data revealed differences in the intracellular carbon fluxes between E. coli cells expressing either VHb or VHb-Red and cells expressing A. eutrophus FHP or the truncated heme domain (FHPg). E. coli MG1655 cells expressing either VHb or VHb-Red were found to function with a branched tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. Furthermore, cellular demands for ATP and reduction equivalents in VHb- and VHb-Red-expressing cells were met by an increased flux through glycolysis. In contrast, in E. coli cells expressing A. eutrophus hemeproteins, the TCA cycle is running cyclically, indicating a shift towards a more aerobic regulation. Consistently, E. coli cells displaying FHP and FHPg activity showed lower production of the typical anaerobic by-products formate, acetate, and D-lactate. The implications of these observations for biotechnological applications are discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Amarasingham C R, Davis B C. Regulation of δ-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase formation in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1965;240:3664–3668. - PubMed
-
- Babul J, Clifton D, Kretschmer M, Fraenkel D G. Glucose metabolism in Escherichia coli and the effect of increased amount of aldolase. Biochemistry. 1993;32:4685–4692. - PubMed
-
- Bailey J E, Sburlati A, Hatzimanikatis V, Lee K, Renner W A, Tsai P S. Inverse metabolic engineering: a strategy for directed genetic engineering of useful phenotypes. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1996;52:109–121. - PubMed
-
- Bax A, Pochapsky S. Optimized recording of heteronuclear multidimensional NMR spectra using pulsed field gradients. J Magn Reson. 1992;99:638–643.
-
- Bergmeyer J, Gassl M. Metabolites 1: carbohydrates. WeinheimWeinheim, Germany: VCH; 1984.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

