Pseudomonas stutzeri nitrite reductase gene abundance in environmental samples measured by real-time PCR
- PMID: 11157241
- PMCID: PMC92645
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.67.2.760-768.2001
Pseudomonas stutzeri nitrite reductase gene abundance in environmental samples measured by real-time PCR
Abstract
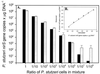
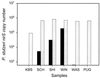
We used real-time PCR to quantify the denitrifying nitrite reductase gene (nirS), a functional gene of biogeochemical significance. The assay was tested in vitro and applied to environmental samples. The primer-probe set selected was specific for nirS sequences that corresponded approximately to the Pseudomonas stutzeri species. The assay was linear from 1 to 10(6) gene copies (r2 = 0.999). Variability at low gene concentrations did not allow detection of twofold differences in gene copy number at less than 100 copies. DNA spiking and cell-addition experiments gave predicted results, suggesting that this assay provides an accurate measure of P. stutzeri nirS abundance in environmental samples. Although P. stutzeri abundance was high in lake sediment and groundwater samples, we detected low or no abundance of this species in marine sediment samples from Puget Sound (Wash.) and from the Washington ocean margin. These results suggest that P. stutzeri may not be a dominant marine denitrifier.
Figures

 , 59 fg; ○, no-template control. CT, cycle at which the fluorescence intensity crosses an arbitrary threshold value. (B) Standard curve. Values represent means ± 95% confidence interval (n = 3).
, 59 fg; ○, no-template control. CT, cycle at which the fluorescence intensity crosses an arbitrary threshold value. (B) Standard curve. Values represent means ± 95% confidence interval (n = 3).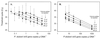


References
-
- Asuming-Brempong S. The effect of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate selection on microbial communities in microcosm and field studies and the impact on ecosystem function. Ph.D. thesis. East Lansing: Michigan State University; 1999.
-
- Bièche I, Laurendeau I, Tozlu S, Olivi M, Vidaud D, Lidereau R, Vidaud M. Quantitation of MYC gene expression in sporadic breast tumors with a real-time reverse transcription-PCR assay. Cancer Res. 1999;59:2759–2765. - PubMed
-
- Bièche I, Olivi M, Champème M-H, Vidaud D, Lidereau R, Vidaud M. Novel approach to quantitative polymerase chain reaction using real-time detection: application to the detection of gene amplification in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1998;78:661–666. - PubMed
-
- Blattner F R, Plunkett III G, Bloch C A, Perna N T, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Vides J, Glasner J D, Rode C K, Mayhew G F, Gregor J, Davis N W, Kirkpatrick H A, Goeden M A, Rose D J, Mau B, Shao Y. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science. 1997;277:1453–1474. - PubMed
-
- Bloem J. Fluorescent staining of microbes for total direct counts. In: Akkermans A D L, van Elsas J D, de Brujin F J, editors. Molecular microbial ecology manual. Dordrecht, The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers; 1995. pp. 1–12.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

