An inducible mouse model for epidermolysis bullosa simplex: implications for gene therapy
- PMID: 11157990
- PMCID: PMC2195993
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.152.3.651
An inducible mouse model for epidermolysis bullosa simplex: implications for gene therapy
Abstract
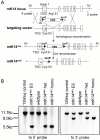
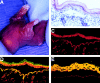
The Dowling-Meara variant of epidermolysis bullosa simplex (EBS-DM) is a severe blistering disease inherited in an autosomal-dominant fashion. Here we report the generation of a mouse model that allows focal activation of a mutant keratin 14 allele in epidermal stem cells upon topical administration of an inducer, resulting in EBS phenotypes in treated areas. Using laser capture microdissection, we show that induced blisters healed by migration of surrounding nonphenotypic stem cells into the wound bed. This observation provides an explanation for the lack of mosaic forms of EBS-DM. In addition, we show that decreased mutant keratin 14 expression resulted in normal morphology and functions of the skin. Our results have important implications for gene therapy of EBS and other dominantly inherited diseases.
Figures





References
-
- Alexeev V., Igoucheva O., Domashenko A., Cotsarelis G., Yoon K. Localized in vivo genotypic and phenotypic correction of the albino mutation in skin by RNA-DNA oligonucleotide. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000;18:43–47. - PubMed
-
- Anton-Lamprecht I., Schnyder U.W. Epidermolysis bullosa herpetiformis Dowling-Meara. Report of a case and pathomorphogenesis. Dermatologica. 1982;164:221–235. - PubMed
-
- Berton T.R., Wang X.J., Zhou Z., Kellendonk C., Schutz G., Tsai S., Roop D.R. Characterization of an inducible, epidermal-specific knockout systemdifferential expression of lacZ in different Cre reporter mouse strains. Genesis. 2000;26:160–161. - PubMed
-
- Chan Y., Anton-Lamprecht I., Yu Q.C., Jackel A., Zabel B., Ernst J.P., Fuchs E. A human keratin 14 “knockout”the absence of K14 leads to severe epidermolysis bullosa simplex and a function for an intermediate filament protein. Genes Dev. 1994;8:2574–2587. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

