Comparative evaluation of semiautomated COBAS AMPLICOR hepatitis B virus (HBV) monitor test and manual microwell plate-based AMPLICOR HBV MONITOR test
- PMID: 11158145
- PMCID: PMC87814
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.2.758-761.2001
Comparative evaluation of semiautomated COBAS AMPLICOR hepatitis B virus (HBV) monitor test and manual microwell plate-based AMPLICOR HBV MONITOR test
Abstract
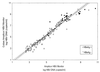
Comparative evaluation of the semiautomated COBAS AMPLICOR hepatitis B virus (HBV) MONITOR Test (COBAS-HBV) and manual AMPLICOR HBV MONITOR Test (AMPLICOR-HBV) on 208 serum samples revealed no significant difference in the sensitivities of the two assays. Twenty samples tested HBV DNA negative and 183 samples tested HBV DNA positive by both assays. Three samples tested positive by COBAS-HBV only and two samples tested positive by AMPLICOR-HBV only. HBV DNA concentrations determined by the two assays were significantly related (n = 183, r = 0.97, P < 0.0001), which indicates that COBAS-HBV could replace AMPLICOR-HBV. The major inconvenience of COBAS-HBV is the required performance of appropriate predilutions of high-titer samples in order to extend the narrow dynamic range of the assay.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of the COBAS TaqMan HBV test with the COBAS Amplicor monitor test for measurement of hepatitis B virus DNA in serum.J Med Virol. 2005 Dec;77(4):486-90. doi: 10.1002/jmv.20481. J Med Virol. 2005. PMID: 16254975
-
Clinical evaluation of the digene hybrid capture II test and the COBAS AMPLICOR monitor test for determination of hepatitis B virus DNA levels.J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Aug;42(8):3513-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.8.3513-3517.2004. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15297491 Free PMC article.
-
Fully automated quantitation of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA in human plasma by the COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan system.J Clin Virol. 2006 Apr;35(4):373-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2006.01.003. Epub 2006 Feb 7. J Clin Virol. 2006. PMID: 16461000
-
Detection and quantitation of HBV DNA in miniaturized samples: multi centre study to evaluate the performance of the COBAS ® AmpliPrep/COBAS ® TaqMan ® hepatitis B virus (HBV) test v2.0 by the use of plasma or serum specimens.J Virol Methods. 2010 Nov;169(2):404-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2010.07.025. Epub 2010 Aug 20. J Virol Methods. 2010. PMID: 20728470
-
An overview of assays for serum HBV DNA.Clin Lab. 2000;46(11-12):609-14. Clin Lab. 2000. PMID: 11109509 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Expertise of laboratories in viral load quantification, genotyping, and precore mutant determination for hepatitis B virus in a multicenter study.J Clin Microbiol. 2006 Oct;44(10):3600-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00732-06. J Clin Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 17021089 Free PMC article.
-
European proficiency testing program for molecular detection and quantitation of hepatitis B virus DNA.J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Dec;39(12):4407-12. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.12.4407-4412.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11724853 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid quantification of hepatitis B virus DNA by automated sample preparation and real-time PCR.J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Jun;42(6):2445-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.6.2445-2449.2004. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15184417 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effect of oxymatrine on serum hepatitis B virus DNA in HBV transgenic mice.World J Gastroenterol. 2004 Apr 15;10(8):1176-9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i8.1176. World J Gastroenterol. 2004. PMID: 15069721 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the COBAS TaqMan 48 real-time PCR system for quantitation of hepatitis B virus DNA.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Jul;43(7):3504-7. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.7.3504-3507.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16000491 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barlet V, Cohard M, Thelu M A, Chaix M J, Baccard C, Zarski J P, Seigneurin J M. Quantification detection of hepatitis B virus DNA in serum using chemiluminescence: comparison with radioactive solution hybridization assay. J Virol Methods. 1994;49:141–152. - PubMed
-
- Berger A, Braner J, Doerr H W, Weber B. Quantification of viral load: clinical relevance for human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B virus and khepatitis C virus infection. Intervirology. 1998;41:24–34. - PubMed
-
- Burk R D, Hwang L Y, Ho G Y F, Shafritz D A, Beasley R P. Outcome of perinatal hepatitis B virus exposure is dependent on maternal virus load. J Infect Dis. 1994;170:1418–1423. - PubMed
-
- Cacciola I, Pollicino T, Squadrito G, Cerenzia G, Villari D, de Franchis R, Santantonio T, Brancatelli S, Colucci G, Raimondo G. Quantification of intrahepatic hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA in patients with chronic HBV infection. Hepatology. 2000;31:507–512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical