p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1) regulate cell cycle reentry after hypoxic stress but are not necessary for hypoxia-induced arrest
- PMID: 11158306
- PMCID: PMC99573
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.21.4.1196-1206.2001
p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1) regulate cell cycle reentry after hypoxic stress but are not necessary for hypoxia-induced arrest
Abstract
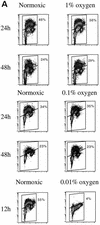
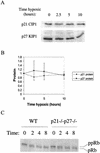
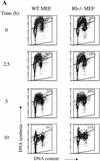
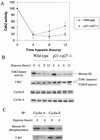
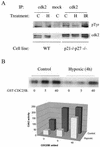
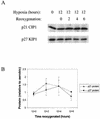
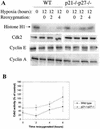
We investigated the role of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1) in cell cycle regulation during hypoxia and reoxygenation. While moderate hypoxia (1 or 0.1% oxygen) does not significantly impair bromodeoxyuridine incorporation, at very low oxygen tensions (0.01% oxygen) DNA replication is rapidly shut down in immortalized mouse embryo fibroblasts. This S-phase arrest is intact in fibroblasts lacking the cyclin kinase inhibitors p21(Cip1) and p27(Kip1), indicating that these molecules are not essential elements of the arrest pathway. Hypoxia-induced arrest is accompanied by dephosphorylation of pRb and inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 2, which results in part from inhibitory phosphorylation. Interestingly, cells lacking the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein also display arrest under hypoxia, suggesting that pRb is not an essential mediator of this response. Upon reoxygenation, DNA synthesis resumes by 3.5 h and reaches aerobic levels by 6 h. Cells lacking p21, however, resume DNA synthesis more rapidly upon reoxygenation than wild-type cells, suggesting that this inhibitor may play a role in preventing premature reentry into the cell cycle upon cessation of the hypoxic stress. While p27 null cells did not exhibit rapid reentry into the cell cycle, cells lacking both p21 and p27 entered S phase even more aggressively than those lacking p21 alone, revealing a possible secondary role for p27 in this response. Cdk2 activity is also restored more rapidly in the double-knockout cells when returned to normoxia. These studies reveal that restoration of DNA synthesis after hypoxic stress, but not the S phase arrest itself, is regulated by p21 and p27.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Involvement of p21(WAF1/Cip1), p27(Kip1), and p18(INK4c) in troglitazone-induced cell-cycle arrest in human hepatoma cell lines.Hepatology. 2001 May;33(5):1087-97. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.24024. Hepatology. 2001. PMID: 11343236
-
Cell cycle exit during terminal erythroid differentiation is associated with accumulation of p27(Kip1) and inactivation of cdk2 kinase.Blood. 2000 Oct 15;96(8):2746-54. Blood. 2000. PMID: 11023508
-
Lovastatin mediated G1 arrest in normal and tumor breast cells is through inhibition of CDK2 activity and redistribution of p21 and p27, independent of p53.Oncogene. 1998 Nov 5;17(18):2393-402. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1202322. Oncogene. 1998. PMID: 9811471
-
New roles for p21 and p27 cell-cycle inhibitors: a function for each cell compartment?Trends Cell Biol. 2003 Feb;13(2):65-70. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(02)00043-0. Trends Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12559756 Review.
-
Cell-cycle inhibitors: three families united by a common cause.Gene. 2000 Apr 18;247(1-2):1-15. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(00)00092-5. Gene. 2000. PMID: 10773440 Review.
Cited by
-
NPP-16/Nup50 function and CDK-1 inactivation are associated with anoxia-induced prophase arrest in Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Biol Cell. 2010 Mar 1;21(5):712-24. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-09-0787. Epub 2010 Jan 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2010. PMID: 20053678 Free PMC article.
-
The regulatory role of HIF-1 in tubular epithelial cells in response to kidney injury.Histol Histopathol. 2020 Apr;35(4):321-330. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-182. Epub 2019 Nov 6. Histol Histopathol. 2020. PMID: 31691948 Review.
-
Notch3 is involved in the proliferation of renal cancer cells via regulation of cell cycle progression and HIF-2α.Oncol Lett. 2020 Dec;20(6):379. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12242. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 33154777 Free PMC article.
-
KSHV-encoded vCyclin can modulate HIF1α levels to promote DNA replication in hypoxia.Elife. 2021 Jul 19;10:e57436. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57436. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34279223 Free PMC article.
-
Tumorigenicity of hypoxic respiring cancer cells revealed by a hypoxia-cell cycle dual reporter.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Aug 26;111(34):12486-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1402012111. Epub 2014 Aug 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25114222 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amellem O, Stokke T, Sandvik J, Pettersen E. The retinoblastoma gene product is reversibly dephosphorylated and bound in the nucleus in S and G2 phases during hypoxic stress. Exp Cell Res. 1996;227:106–115. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P, Dor Y, Herbert J M, Fukumura D, Brusselmans K, Dewerchin M, Neeman M, Bono F, Abramovitch R, Maxwell P, Koch C J, Ratcliffe P, Moons L, Jain R K, Collen D, Keshert E. Role of HIF-1alpha in hypoxia-mediated apoptosis, cell proliferation and tumour angiogenesis. Nature. 1998;394:485–490. . (Erratum, 395:525.) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
