CYP83B1, a cytochrome P450 at the metabolic branch point in auxin and indole glucosinolate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 11158532
- PMCID: PMC102201
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.13.1.101
CYP83B1, a cytochrome P450 at the metabolic branch point in auxin and indole glucosinolate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis
Abstract
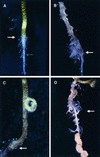
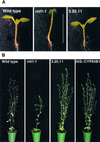
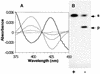
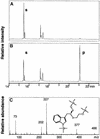
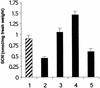
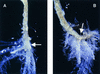
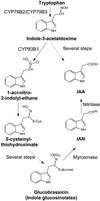
Auxins are growth regulators involved in virtually all aspects of plant development. However, little is known about how plants synthesize these essential compounds. We propose that the level of indole-3-acetic acid is regulated by the flux of indole-3-acetaldoxime through a cytochrome P450, CYP83B1, to the glucosinolate pathway. A T-DNA insertion in the CYP83B1 gene leads to plants with a phenotype that suggests severe auxin overproduction, whereas CYP83B1 overexpression leads to loss of apical dominance typical of auxin deficit. CYP83B1 N-hydroxylates indole-3-acetaldoxime to the corresponding aci-nitro compound, 1-aci-nitro-2-indolyl-ethane, with a K(m) of 3 microM and a turnover number of 53 min(-1). The aci-nitro compound formed reacts non-enzymatically with thiol compounds to produce an N-alkyl-thiohydroximate adduct, the committed precursor of glucosinolates. Thus, indole-3-acetaldoxime is the metabolic branch point between the primary auxin indole-3-acetic acid and indole glucosinolate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis.
Figures
Comment in
-
New insights into auxin biosynthesis.Plant Cell. 2001 Jan;13(1):1-3. doi: 10.1105/tpc.13.1.1. Plant Cell. 2001. PMID: 11158524 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Andersen, M.D., Busk, P.K., Svendsen, I., and Møller, B.L. (2000). Cytochromes P450 from cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) catalyzing the first steps in the biosynthesis of the cyanogenic glucosides linamarin and lotaustralin. Cloning, functional expression in Pichia pastoris, and substrate specificity of the isolated recombinant enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 275 1966–1977. - PubMed
-
- Bak, S., Kahn, R.A., Nielsen, H.L., Møller, B.L., and Halkier, B.A. (1998. a). Cloning of three A-type cytochromes P450, CYP71E1, CYP98, and CYP99 from Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench by a PCR approach and identification by expression in Escherichia coli of CYP71E1 as a multifunctional cytochrome P450 in the biosynthesis of the cyanogenic glucoside dhurrin. Plant Mol. Biol. 36 393–405. - PubMed
-
- Bak, S., Nielsen, H.L., and Halkier, B.A. (1998. b). The presence of CYP79 homologues in glucosinolate-producing plants shows evolutionary conservation of the enzymes in the conversion of amino acids til aldoxime in the biosynthesis of cyanogenic glucosides and glucosinolates. Plant Mol. Biol. 38 725–734. - PubMed
-
- Bak, S., Olsen, C.E., Petersen, B.L., Møller, B.L., and Halkier, B.A. (1999). Metabolic engineering of p-hydroxybenzylglucosinolate in Arabidopsis by expression of the cyanogenic CYP79A1 from Sorghum bicolor. Plant J. 20 663–671. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

