Molecular clocks
- PMID: 11158575
- PMCID: PMC14689
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.98.3.944
Molecular clocks
Abstract
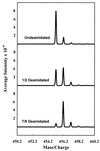
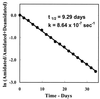
A convenient and precise mass spectrometric method for measurement of the deamidation rates of glutaminyl and asparaginyl residues in peptides and proteins has been developed; the rates of deamidation of 306 asparaginyl sequences in model peptides at pH 7.4, 37.0 degrees C, 0.15 M Tris.HCl buffer have been determined; a library of 913 amide-containing peptides for use by other investigators in similar studies has been established; and, by means of simultaneous deamidation rate measurements of rabbit muscle aldolase and appropriate model peptides in the same solutions, the use of this method for quantitative measurement of the relative effects of primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary protein structure on deamidation rates has been demonstrated. The measured rates are discussed with respect to the hypothesis that glutaminyl and asparaginyl residues serve, through deamidation, as molecular timers of biological events.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

