Bactericidal activities of two daptomycin regimens against clinical strains of glycopeptide intermediate-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium, and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model with simulated endocardial vegetations
- PMID: 11158740
- PMCID: PMC90312
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.45.2.454-459.2001
Bactericidal activities of two daptomycin regimens against clinical strains of glycopeptide intermediate-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium, and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in an in vitro pharmacodynamic model with simulated endocardial vegetations
Abstract
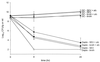
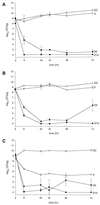
Daptomycin is an investigational lipopeptide antibiotic active against gram-positive organisms. The mechanism of action is unique, resulting in interference with cell membrane transport. The bactericidal activity of daptomycin was evaluated against glycopeptide-intermediate susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (GISA), vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium (VREF), and methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) in an in vitro infection model with simulated endocardial vegetations. Simulated regimens of daptomycin at 6 mg/kg/day (D6) and 10 mg/kg/day (D10) were utilized. MICs and MBCs for daptomycin were determined in the absence and in the presence of albumin with the following results (MIC/MBC): for GISA-992, 0.5/1.0 and 16/16; for VREF-590, 2.0/2.0 and 32/32; and for MRSA-494, 0.25/0.25 and 1.0/4.0 microg/ml, respectively. During the first 8 h daptomycin significantly reduced the inoculum for all organisms. Daptomycin at 6 mg/kg/day and 10 mg/kg/day had log(10) CFU/g reductions of 5 and 6, 3.4 and 5, and 6.4 and 6.5 by 8 h for GISA-992, VREF-590, and MRSA-494, respectively. Against both GISA-992 and VREF-590, the D10 regimen achieved the limit of detection at 72 h, with D6 regimens showing slight regrowth. A concentration-dependent killing effect was noted to occur, with daptomycin demonstrating a more rapid and greater kill from the D10 versus the D6 regimen. The results of this study suggest that daptomycin demonstrates significant (P < 0.05) activity against gram-positive organisms in a simulated sequestered infection site.
Figures
References
-
- Anonymous. Interim guidelines for prevention and control of staphylococcal infection associated with reduced susceptibility to vancomycin. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1997;46:626–628. ,635. - PubMed
-
- Caron F, Carbon C, Gutmann L. Triple-combination penicillin-vancomycin-gentamicin for experimental endocarditis caused by a moderately penicillin- and highly glycopeptide-resistant isolate of Enterococcus faecium. J Infect Dis. 1991;164:888–893. - PubMed
-
- Caron F, Kitzis M D, Gutmann L, Cremieux A C, Maziere B, Vallois J M, Saleh-Mghir A, Lemeland J F, Carbon C. Daptomycin or teicoplanin in combination with gentamicin for treatment of experimental endocarditis due to a highly glycopeptide-resistant isolate of Enterococcus faecium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992;36:2611–2616. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Summary of notifiable diseases, United States. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1998;47:19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

