Identification of the corticospinal tracts achieved using blood-oxygen-level-dependent and diffusion functional MR imaging in patients with brain tumors
- PMID: 11158892
- PMCID: PMC7975563
Identification of the corticospinal tracts achieved using blood-oxygen-level-dependent and diffusion functional MR imaging in patients with brain tumors
Abstract
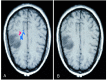
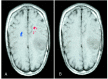
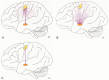
Diffusion-weighted MR imaging was used to delineate the corticospinal tract (CST) successfully and to depict its relationship to adjacent brain tumors. The CST was defined by a method by which it seems possible to delimit the distance from the CST to the main tumor mass and to show displacement and infiltration of the tract by the neoplasia. This information cannot be gathered from routine anatomic MR imaging.
Figures

References
-
- Maldjian JA, Schulder M, Liu WC, et al. Intraoperative functional MRI using a real-time neurosurgical navigation system. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1997;21:910-912 - PubMed
-
- Schulder M, Maldjian JA, Liu WC, et al. Functional image-guided surgery of intracranial tumors located in or near the sensorimotor cortex. J Neurosurg 1998;89:412-418 - PubMed
-
- Rezai AR, Hund M, Kronberg E, et al. The interactive use of magnetoencephalography in stereotactic image-guided neurosurgery. Neurosurgery 1996;39:92-102 - PubMed
-
- Jack CR, Thompson RM, Butts RK, et al. Sensory motor cortex: correlation of presurgical mapping with functional MR imaging and invasive cortical mapping. Radiology 1994;190:85-92 - PubMed
-
- Atlas SW, Howard RS, Maldjian JA, et al. Functional magnetic resonance imaging of regional brain activity in patients with intracerebral gliomas: findings and implications for clinical management. Neurosurgery 1996;38:329-338 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
