Disruption of nuclear factor-interleukin-6, a transcription factor, results in severe mycobacterial infection
- PMID: 11159172
- PMCID: PMC1850332
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63977-6
Disruption of nuclear factor-interleukin-6, a transcription factor, results in severe mycobacterial infection
Abstract
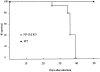
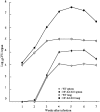
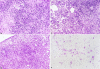
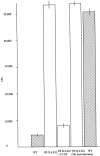
Nuclear factor-interleukin-6 (NF-IL-6) is one of several nuclear transcription factors (NF-IL-6, NF-kappaB, PU.1, interferon-regulatory factor 1, Egr-1, and Stat-1). NF-IL-6 and NF-kappaB are expressed in macrophages and is induced by bacterial lipopolysaccharides. To evaluate whether NF-IL-6 is required for the inflammatory immune response to mycobacterial infection, in which epithelioid macrophages comprise the leading cell population, we generated NF-IL-6 knockout (KO) mutant mice. Airborne infection of these mice with Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains induced disseminated tuberculosis lacking granuloma formation, although interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and interleukin-12 mRNA expression levels were within the normal range compared with those of wild-type mice. Generation of O2- and mycobacterial killing by neutrophils from these mice were impaired severely compared with wild-type mice. We conclude that NF-IL-6 is a critical transcription factor in mycobacterial control as well as in granulocyte-colony stimulating factor induction resulting in neutrophil activation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Relative importance of NF-kappaB p50 in mycobacterial infection.Infect Immun. 2001 Nov;69(11):7100-5. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.11.7100-7105.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11598086 Free PMC article.
-
Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in Mycobacterium-induced granuloma formation in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-deficient mice.Lab Invest. 1999 Apr;79(4):379-86. Lab Invest. 1999. PMID: 10211990
-
Macrophages are a significant source of type 1 cytokines during mycobacterial infection.J Clin Invest. 1999 Apr;103(7):1023-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI6224. J Clin Invest. 1999. PMID: 10194475 Free PMC article.
-
Role of STAT1, NF-kappaB, and C/EBPbeta in the macrophage transcriptional regulation of hepcidin by mycobacterial infection and IFN-gamma.J Leukoc Biol. 2009 Nov;86(5):1247-58. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1208719. Epub 2009 Aug 3. J Leukoc Biol. 2009. PMID: 19652026
-
Immunotherapy of mycobacterial infections.Semin Respir Infect. 2001 Mar;16(1):47-59. doi: 10.1053/srin.2001.22728. Semin Respir Infect. 2001. PMID: 11309712 Review.
Cited by
-
Arabinogalactan enhances Mycobacterium marinum virulence by suppressing host innate immune responses.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 26;13:879775. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.879775. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36090984 Free PMC article.
-
Relative importance of NF-kappaB p50 in mycobacterial infection.Infect Immun. 2001 Nov;69(11):7100-5. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.11.7100-7105.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11598086 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological and immunological profiles of rat tuberculosis.Int J Exp Pathol. 2004 Jun;85(3):125-34. doi: 10.1111/j.0959-9673.2004.00379.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15255966 Free PMC article.
-
Rat neutrophils prevent the development of tuberculosis.Infect Immun. 2004 Mar;72(3):1804-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.72.3.1804-1806.2004. Infect Immun. 2004. PMID: 14977991 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid therapy attenuates the severity of tuberculosis while altering lymphocyte and macrophage numbers and cytokine expression in rats infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Nutr. 2007 Dec;137(12):2696-700. doi: 10.1093/jn/137.12.2696. J Nutr. 2007. PMID: 18029486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Natsuka S, Akira S, Nishio Y, Hashimoto S, Sugita T, Isshiki H, Kishimoto T: Macrophage differentiation specific expression of NF-IL-6, a transcription factor for IL-6. Blood 1992, 79:460-466 - PubMed
-
- Scott LM, Civin CI, Rorth P, Friedman AD: A novel temporal expression pattern of three C/EBP family members in differentiating myelomonocytic cells. Blood 1992, 80:1725-1735 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

