Effect of chronic morphine treatment on alpha(2)-adrenoceptor mediated autoinhibition of transmitter release from sympathetic varicosities of the mouse vas deferens
- PMID: 11159688
- PMCID: PMC1572583
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703842
Effect of chronic morphine treatment on alpha(2)-adrenoceptor mediated autoinhibition of transmitter release from sympathetic varicosities of the mouse vas deferens
Abstract
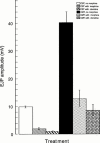
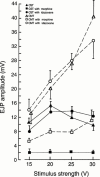
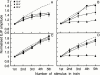
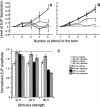
1. The effect of chronic morphine treatment (CMT) on sympathetic innervation of the mouse vas deferens and on alpha(2)-adrenoceptor mediated autoinhibition has been examined using intracellular recording of excitatory junction potentials (EJPs) and histochemistry. 2. In chronically saline treated (CST) preparations, morphine (1 microM) and the alpha(2)-adrenoceptor agonist (clonidine, 1 microM) decreased the mean amplitude of EJPs evoked with 0.03 Hz stimulation by 81+/-8% (n=16) and 92+/-6% (n=7) respectively. In CMT preparations, morphine (1 microM) and clonidine (1 microM) decreased mean EJP amplitude by 68+/-8% (n=7) and 79+/-8% (n=7) respectively. 3. When stimulating the sympathetic axons at 0.03 Hz, the mean EJP amplitude recorded from smooth muscles acutely withdrawn from CMT was four times greater than for CST smooth muscles (40.7+/-3.8 mV, n=7 compared with 9.9+/-0.3 mV, n=7). 4. Part of the increase in mean EJP amplitude following CMT was produced by a 31% increase in the density of sympathetic axons and varicosities innervating the smooth muscle. 5. Results from the present study indicate that the effectiveness of alpha(2)-adrenoceptor mediated autoinhibition is only slightly reduced in CMT preparations. Most of the cross tolerance which develops between morphine, clonidine and alpha(2)-adrenoceptor mediated autoinhibition occurs as a consequence of increased efficacy of neuromuscular transmission which is produced by an increase in the probability of transmitter release and an increase in the density of sympathetic innervation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of chronic clonidine treatment on transmitter release from sympathetic varicosities of the guinea-pig vas deferens.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Dec;134(7):1480-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704383. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11724754 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of chronic morphine treatment on transmitter release from sympathetic varicosities of the mouse vas deferens.Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Dec;116(7):2860-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb15937.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 8680717 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of morphine on the nerve terminal impulse and transmitter release from sympathetic varicosities innervating the mouse vas deferens.Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Dec;116(7):2852-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb15936.x. Br J Pharmacol. 1995. PMID: 8680716 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotransmitter release mechanisms in sympathetic neurons: past, present, and future perspectives.Neurochem Res. 2001 Sep;26(8-9):875-89. doi: 10.1023/a:1012320130988. Neurochem Res. 2001. PMID: 11699939 Review.
-
Transmitter release from sympathetic nerve terminals on an impulse-by-impulse basis and presynaptic receptors.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;604:176-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb31992.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990. PMID: 1977347 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Neuroeffector Ca2+ transients for the direct measurement of purine release and indirect measurement of cotransmitters in rodents.Exp Physiol. 2009 Jan;94(1):25-30. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2008.043679. Epub 2008 Sep 19. Exp Physiol. 2009. PMID: 18805863 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of chronic clonidine treatment on transmitter release from sympathetic varicosities of the guinea-pig vas deferens.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Dec;134(7):1480-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704383. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11724754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ALGUACIL L.F., ALAMO C., SANTOS C., CUENCA E. Yohimbine reduces morphine tolerance in guinea-pig ileum. Life Sci. 1987;40:155–160. - PubMed
-
- ALLGAIER C., DASCHMANN B., SIEVERLING J., HERTTING G. Presynaptic k-receptors on noradrenergic nerve terminals couple to G proteins and interact with the α2-adrenoceptors. J. Neurochem. 1989;53:1629–1635. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

