Evidence for cocaine and methylecgonidine stimulation of M(2) muscarinic receptors in cultured human embryonic lung cells
- PMID: 11159694
- PMCID: PMC1572570
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703819
Evidence for cocaine and methylecgonidine stimulation of M(2) muscarinic receptors in cultured human embryonic lung cells
Abstract
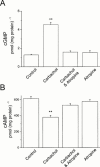
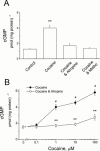
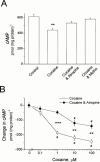
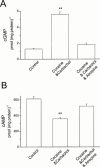
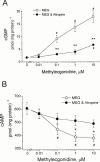
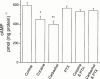
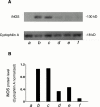
1. Muscarinic cholinoceptor stimulation leads to an increase in guanylyl cyclase activity and to a decrease in adenylyl cyclase activity. This study examined the effects of cocaine and methylecgonidine (MEG) on muscarinic receptors by measurement of cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP content in cultured human embryonic lung (HEL299) cells which specifically express M(2) muscarinic receptors. 2. A concentration-dependent increase in cyclic GMP production was observed in HEL299 cells incubated with carbachol, cocaine, or MEG for 24 h. The increase in cyclic GMP content was 3.6 fold for 1 microM carbachol (P < 0.01), 3.1 fold for 1 microM cocaine (P < 0.01), and 7.8 fold for 1 microM MEG (P < 0.001), respectively. This increase in cyclic GMP content was significantly attenuated or abolished by the muscarinic receptor antagonist atropine or the M(2) blocker methoctramine. 3. In contrast, cocaine, MEG, and carbachol produced a significant inhibition of cyclic AMP production in HEL299 cells. Compared to the control, HEL299 cells treated with 1 microM cocaine decreased cyclic AMP production by 30%. MEG and carbachol at 1 microM decreased cyclic AMP production by 37 and 38%, respectively. Atropine or methoctramine at 1 or 10 microM significantly attenuated or abolished the cocaine-induced decrease in cyclic AMP production. However, the antagonists alone had neither an effect on cyclic GMP nor cyclic AMP production. Pretreatment of HEL299 cells with pertussis toxin prevented the cocaine-induced reduction of cyclic AMP production. 4. Western blot analysis showed that HEL299 cells specifically express M(2) muscarinic receptors without detectable M(1) and M(3). Incubation of HEL299 cells with cocaine, carbachol, and atropine did not alter the expression of M(2) protein levels. However, the inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) was induced in the presence of cocaine or carbachol and this induction was significantly attenuated after addition of atropine or methoctramine. 5. The present data show that cocaine and MEG significantly affect cyclic GMP and cyclic AMP production in cultured HEL299 cells. Our results also show that these effects result from the drug-induced stimulation of M(2) muscarinic receptors accompanied with no alterations of receptor expression. However, the induction of iNOS by cocaine may result in the increase in cyclic GMP production.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enhancement of nitric oxide production by methylecgonidine in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Jan;135(1):188-96. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704414. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11786494 Free PMC article.
-
Dual effects of muscarinic M(2) acetylcholine receptors on the synthesis of cyclic AMP in CHO cells: dependence on time, receptor density and receptor agonists.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Mar;132(6):1217-28. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703931. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11250872 Free PMC article.
-
Muscarinic cholinergic stimulation of the nitric oxide-cyclic GMP signaling system in cultured rat sensory neurons.Neuroscience. 1994 Sep;62(2):351-9. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90370-0. Neuroscience. 1994. PMID: 7530344
-
Muscarinic regulation of the L-type calcium current in isolated cardiac myocytes.Life Sci. 1997;60(13-14):1113-20. doi: 10.1016/s0024-3205(97)00055-6. Life Sci. 1997. PMID: 9121355 Review.
-
Biochemical characterization of the muscarinic receptors.Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1983;55:137-96. doi: 10.1002/9780470123010.ch2. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1983. PMID: 6312781 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Enhancement of nitric oxide production by methylecgonidine in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Jan;135(1):188-96. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704414. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11786494 Free PMC article.
-
Anhydroecgonine Methyl Ester (AEME), a Product of Cocaine Pyrolysis, Impairs Spatial Working Memory and Induces Striatal Oxidative Stress in Rats.Neurotox Res. 2018 Nov;34(4):834-847. doi: 10.1007/s12640-017-9813-y. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Neurotox Res. 2018. PMID: 28914428
-
The muscarinic effect of anhydroecgonine methyl ester, a crack cocaine pyrolysis product, impairs melatonin synthesis in the rat pineal gland.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2017 Mar 29;6(4):420-431. doi: 10.1039/c7tx00009j. eCollection 2017 Jul 1. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2017. PMID: 30090510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BENCHIMOL A., BARTALL H., DESSER K.B. Accelerated ventricular rhythm and cocaine abuse. Ann. Intern. Med. 1978;88:519–520. - PubMed
-
- BILLMAN G.E., LOPPI M.D. Effects of cocaine on cardiac vagal tone before and during coronary artery occlusion: cocaine exacerbate the autonomic response to myocardial ischemia. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1993;22:869–876. - PubMed
-
- CHAMBERS H.F., MORRIS D.L., TAUBER M.G., MODIN G. Cocaine use and the risk for endocarditis in intravenous drug users. Ann. Intern. Med. 1987;106:833–836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

