Mediator involvement in antigen-induced bronchospasm and microvascular leakage in the airways of ovalbumin sensitized Brown Norway rats
- PMID: 11159698
- PMCID: PMC1572587
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703847
Mediator involvement in antigen-induced bronchospasm and microvascular leakage in the airways of ovalbumin sensitized Brown Norway rats
Abstract
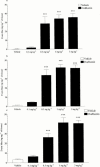
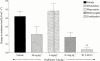
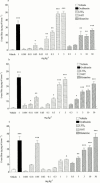
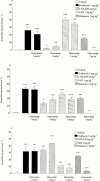
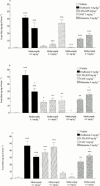
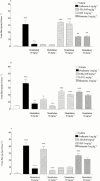
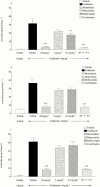
1. To determine which mediators are involved in antigen-induced bronchospasm and microvascular leakage in the airways of ovalbumin sensitised Brown Norway rats we investigated the effect of a histamine H(1) receptor antagonist, mepyramine, a 5-HT receptor antagonist, methysergide, and a cys-leukotriene-1 receptor antagonist, montelukast. 2. Ovalbumin at 1 mg kg(-1) i.v. caused a significant increase in microvascular leakage in the airways and at 3 mg kg(-1) i.v. caused a significant increase in airways resistance. 3. Histamine (1 mg kg(-1) i.v.), 5-HT (0.1 mg kg(-1) i.v.) and leukotriene D(4) (LTD(4), 50 microg kg(-1) i.v.) caused a significant increase in microvascular leakage in the airways. 4. Mepyramine (1 mg kg(-1) i.v.), methysergide (0.1 mg kg(-1) i.v.), or montelukast (30 mg kg(-1) i.v.) inhibited histamine, 5-HT or LTD(4) -induced microvascular leakage respectively. 5. Methysergide (0.1 mg kg(-1) i.v.) reduced ovalbumin-induced microvascular leakage in the trachea and at 0.3 mg kg(-1) i.v. inhibited bronchospasm (38 and 58%, respectively). Montelukast (30 mg kg(-1) p.o.) reduced ovalbumin-induced microvascular leakage in airway tissue to basal levels (78%) and inhibited ovalbumin-induced bronchospasm (50%). Mepyramine (3 mg kg(-1) i.v.) had no effect on ovalbumin-induced leakage or bronchospasm. 6. A combination of all three compounds (mepyramine, methysergide and montelukast) reduced ovalbumin-induced microvascular leakage in airway tissue to basal levels (70 - 78%) and almost completely inhibited bronchospasm (92%). 7. Antigen-induced bronchospasm appears to equally involve the activation of 5-HT and cys-leukotriene-1 receptors whereas ovalbumin-induced microvascular leakage appears to be predominantly mediated by cys-leukotriene-1 receptors.
Figures
References
-
- BEL E.H., VAN DER VEEN H., KRAMPS J.A., DIJKMAN J.H., STERK P.J. Maximal airway narrowing to inhaled leukotriene D4 in normal subjects. Comparison and interaction with methacholine. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1987;136:979–984. - PubMed
-
- BERNAREGGI M., MITCHELL J.A., BARNES P.J., BELVISI M.G. Dual action of nitric oxide on airway plasma leakage. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997;155:869–874. - PubMed
-
- CHUNG K.F., ROGERS D.F., BARNES P.J., EVANS T.W. The role of increased airway microvascular permeability and plasma exudation in asthma. Eur. Resp. J. 1990;3:329–337. - PubMed
-
- DAHLEN S.E., BJORK J., HEDQVIST P., ARFORS K.E., HAMMARSTROM S., LINDGREN J.A., SAMUELSSON B. Leukotrienes promote plasma leakage and leukocyte adhesion in postcapillary venules: in vivo effects with relevance to the acute inflammatory response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1981;78:3387–3391. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

