Rasagiline [N-propargyl-1R(+)-aminoindan], a selective and potent inhibitor of mitochondrial monoamine oxidase B
- PMID: 11159700
- PMCID: PMC1572573
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703826
Rasagiline [N-propargyl-1R(+)-aminoindan], a selective and potent inhibitor of mitochondrial monoamine oxidase B
Abstract
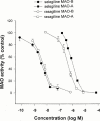
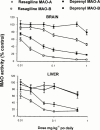
1. Rasagiline [N-propargyl-1R(+)-aminoindan], was examined for its monoamine oxidase (MAO) A and B inhibitor activities in rats together with its S(-)-enantiomer (TVP 1022) and the racemic compound (AGN-1135) and compared to selegiline (1-deprenyl). The tissues that were studied for MAO inhibition were the brain, liver and small intestine. 2. While rasagiline and AGN1135 are highly potent selective irreversible inhibitors of MAO in vitro and in vivo, the S(-) enantiomer is relatively inactive in the tissues examined. 3. The in vitro IC(50) values for inhibition of rat brain MAO activity by rasagiline are 4.43+/-0.92 nM (type B), and 412+/-123 nM (type A). The ED(50) values for ex vivo inhibition of MAO in the brain and liver by a single dose of rasagiline are 0.1+/-0.01, 0.042+/-0.0045 mg kg(-1) respectively for MAO-B, and 6.48+/-0.81, 2.38+/-0.35 mg kg(-1) respectively for MAO-A. 4. Selective MAO-B inhibition in the liver and brain was maintained on chronic (21 days) oral dosage with ED(50) values of 0.014+/-0.002 and 0.013+/-0.001 mg kg(-1) respectively. 5. The degree of selectivity of rasagiline for inhibition of MAO-B as opposed to MAO-A was similar to that of selegiline. Rasagiline was three to 15 times more potent than selegiline for inhibition of MAO-B in rat brain and liver in vivo on acute and chronic administration, but had similar potency in vitro. 6. These data together with lack of tyramine sympathomimetic potentiation by rasagiline, at selective MAO-B inhibitory dosage, indicate that this inhibitor like selegiline may be a useful agent in the treatment of Parkinson's disease in either symptomatic or L-DOPA adjunct therapy, but lack of amphetamine-like metabolites could present a therapeutic advantage for rasagiline.
Figures


References
-
- BIRKMAYER W., RIEDERER P., AMBROZI L., YOUDIM M.B.H. Implications of combined treatment with Madopar and 1-deprenyl in Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 1977;2:439–443. - PubMed
-
- BIRKMAYER W., RIEDERER P., YOUDIM M.B.H., LINAUER W. The potentiation of anti-akinetic effect after L-dopa treatment by an inhibitor of MAO-B, deprenyl. J. Neural Transm. 1975;36:303–326. - PubMed
-
- COLLINS G.G.S., SANDLER M., WILLIAMS E.D., YOUDIM M.B.H. Multiple forms of human brain mitochondrial monoamine oxidase. Nature. 1970;225:817–820. - PubMed
-
- DELLA CORTE L., TIPTON K.F. The turnover of the A and B-forms of monoamine oxidase in rat liver. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1980;29:811–815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

