Effects of extracellular nucleotides and nucleosides on prostate carcinoma cells
- PMID: 11159704
- PMCID: PMC1572579
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703833
Effects of extracellular nucleotides and nucleosides on prostate carcinoma cells
Abstract
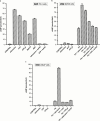
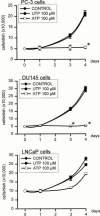
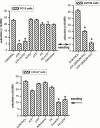
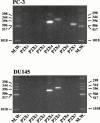
1. The purpose of this work was to characterize the receptors involved in the action of nucleotides on the human prostate carcinoma cell lines LNCaP, PC-3 and DU145. 2. Northern blotting revealed the presence of P2Y(2), P2Y(6) and P2Y(11) messengers in the three cell lines. P2Y(1) mRNA was only observed in the DU145 cells. In both PC-3 and DU145 cells, ATP and UTP stimulated inositol phosphate accumulation in an equipotent, equiactive and non-additive way, suggesting the involvement of P2Y(2) receptors. ATP also increased cyclic AMP, but this effect is likely to result from degradation into adenosine and activation of A(2) receptor. A(2) receptor activation led to a synergistic enhancement of prostate-specific antigen secretion induced by vasoactive intestinal peptide. 3. RT - PCR experiments detected the expression of the P2X(4) and P2X(5) receptors in the DU145 cells and the P2X(4), P2X(5) and P2X(7) receptors in the PC-3 cells. The calcium influx induced by BzATP confirmed the functional expression of P2X receptors. 4. ATP inhibited the growth of PC-3 and DU145 cells. This effect was mimicked neither by UTP nor by adenosine, indicating that it does not result from phospholipase C or adenylyl cyclase activation. On the contrary, in PC-3 cells, BzATP reproduced the effect of ATP, which was associated to a moderate decrease of proliferation and an increase of apoptosis. In DU145 cells, ATP was more potent than BzATP and growth inhibition was mainly associated with necrosis. We suggest that P2X receptors might be involved in the inhibition by nucleotides of prostate carcinoma cell growth.
Figures

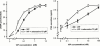

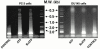

Similar articles
-
Characterization of calcium-independent purinergic receptor-mediated apoptosis in hormone-refractory prostate cancer.BJU Int. 2008 Feb;101(3):352-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2007.07293.x. Epub 2007 Nov 13. BJU Int. 2008. PMID: 18005209
-
Extracellular ATP-induced calcium signaling in mIMCD-3 cells requires both P2X and P2Y purinoceptors.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004 Aug;287(2):F204-14. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00281.2003. Epub 2004 Apr 6. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15068972
-
Osteoblast responses to nucleotides increase during differentiation.Bone. 2006 Aug;39(2):300-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2006.02.063. Epub 2006 Apr 17. Bone. 2006. PMID: 16616882
-
Extracellular nucleotide signaling in the inner ear.Mol Neurobiol. 1998 Feb;16(1):21-48. doi: 10.1007/BF02740601. Mol Neurobiol. 1998. PMID: 9554700 Review.
-
Roles of extracellular nucleotides and P2 receptors in ectodomain shedding.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Nov;73(22):4159-4173. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2274-2. Epub 2016 May 14. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27180276 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Short- and long-term (trophic) purinergic signalling.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016 Aug 5;371(1700):20150422. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2015.0422. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27377731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis and preclinical validation of novel P2Y1 receptor ligands as a potent anti-prostate cancer agent.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 12;9(1):18938. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55194-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31831761 Free PMC article.
-
P2Y2 receptor activation by nucleotides released from highly metastatic breast cancer cells increases tumor growth and invasion via crosstalk with endothelial cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Aug 26;16(5):R77. doi: 10.1186/bcr3694. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25156554 Free PMC article.
-
Purinergic signalling and cancer.Purinergic Signal. 2013 Dec;9(4):491-540. doi: 10.1007/s11302-013-9372-5. Purinergic Signal. 2013. PMID: 23797685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term (trophic) purinergic signalling: purinoceptors control cell proliferation, differentiation and death.Cell Death Dis. 2010;1(1):e9. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2009.11. Cell Death Dis. 2010. PMID: 21364628 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- ABBRACHIO M.P., BURNSTOCK G. Purinoceptors: are there families of P2X and P2Y purinoceptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 1994;64:445–475. - PubMed
-
- BRAKE A.J., WAGENBACH M.J., JULIUS D. New structural motif for ligand-gated ion channels defined by an ionotrophic ATP receptor. Nature. 1994;371:519–523. - PubMed
-
- BROOKER G., HARPER J.F., TERASEKI W.L., MOYLAN R.D. Radioimmunoassay of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP. Adv. Cyclic Nucleotides Res. 1979;10:1–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

