alpha(4) integrin-dependent eosinophil recruitment in allergic but not non-allergic inflammation
- PMID: 11159710
- PMCID: PMC1572591
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703857
alpha(4) integrin-dependent eosinophil recruitment in allergic but not non-allergic inflammation
Abstract
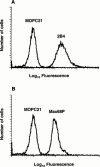
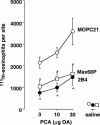
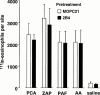
1. Although anti-alpha(4) integrin mAbs reduce eosinophil accumulation in several models of allergic inflammation, it is not clear whether this occurs via a direct action to block eosinophil alpha(4) integrins or indirectly on another cell type. The role of alpha(4) integrins on the accumulation of (111)In-labelled eosinophils in allergic and non-allergic inflammation in guinea-pig skin was therefore investigated. 2. Intradermal injection of antigen in sensitized skin sites induced accumulation of (111)In-eosinophils that was reduced up to 70% by two anti-alpha(4) integrin mAbs. In contrast, accumulation of (111)In-eosinophils to intradermal chemoattractants was unaffected by the same mAbs. 3. Accumulation of (111)In-eosinophils in allergic and non-allergic conditions was partly inhibited by a low dose of an anti-beta(2) integrin mAb. In combination with anti-alpha(4) integrin mAb, responses were not further reduced suggesting that these adhesion pathways are not additive or synergic. 4. Pretreating skin sites with antiserum or contaminating LPS did not reveal an alpha(4) integrin dependent pathway for chemoattractant-induced (111)In-eosinophil accumulation. These data suggest that alpha(4) integrins are involved in the response to antigen in sensitized skin sites. 5. Pretreating (111)In-eosinophil with alpha(4) integrin mAb blocked their adhesion to fibronectin in vitro but did not inhibit their accumulation in allergic inflammation suggesting that the blocking effect in vivo was eosinophil independent. 6. These data support the concept that targeting alpha(4) integrins on cells other than eosinophils could control eosinophil accumulation and have therapeutic potential in allergic diseases such as asthma and atopic dermatitis.
Figures
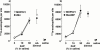
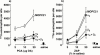
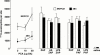
Similar articles
-
Priming and induction of eosinophil trafficking in guinea-pig cutaneous inflammation by tumour necrosis factor alpha.Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Nov;125(6):1228-35. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702224. Br J Pharmacol. 1998. PMID: 9863651 Free PMC article.
-
IL-4-induced eosinophil accumulation in rat skin is dependent on endogenous TNF-alpha and alpha 4 integrin/VCAM-1 adhesion pathways.J Immunol. 1998 Jun 1;160(11):5637-45. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9605170
-
Human eotaxin induces alpha 4 and beta 2 integrin-dependent eosinophil accumulation in rat skin in vivo: delayed generation of eotaxin in response to IL-4.J Immunol. 1998 Apr 1;160(7):3569-76. J Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9531320
-
The role of alpha 4 integrins in lung pathophysiology.Eur Respir J Suppl. 1996 Aug;22:104s-108s. Eur Respir J Suppl. 1996. PMID: 8871053 Review.
-
The effect of anti-integrin monoclonal antibodies on antigen-induced pulmonary inflammation in allergic rabbits.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2003;16(5):279-85. doi: 10.1016/S1094-5539(03)00069-5. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2003. PMID: 12877819 Review.
References
-
- ABRAHAM W.M., AHMED A., SIELCZAK M.W., NARITA M., ARRHENIUS T., ELICES M.J. Blockade of late-phase airway responses and airway hyperresponsiveness in allergic sheep with a small-molecule peptide inhibitor of VLA-4. Am. J. Resp. Crit. Care Med. 1997;156:696–703. - PubMed
-
- ANDREW D., SHOCK A., BALL E., ORTLEPP S., BELL J., ROBINSON M. KIM185, a monoclonal antibody to CD18 which induces a change in the conformation of CD18 and promotes both LFA-1- and CR3-dependent adhesion. Eur. J. Immunol. 1993;23:2217–2222. - PubMed
-
- BLEASE K., SEYBOLD J., ADCOCK I., HELLEWELL P.G., BURKE-GAFFNEY A.C. Interleukin-4 and LPS synergise to induce vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 expression in human lung microvascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Resp. Cell. Mol. Biol. 1998;18:620–630. - PubMed
-
- CHIN J.E., HATFIELD C.A., WINTERROWD G.E., BRASHLER J.R., VONDERFECHT S.L., FIDLER S.F., GRIFFIN R.L., KOLBASA K.P., KRZESICKI R.F., SLY L.M., STAITE N.D., RICHARDS I.M. Airway recruitment of leukocytes in mice is dependent on alpha4-integrins and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Am. J. Physiol. 1997;272:L219–L229. - PubMed
-
- COLUMBO M., BOCHNER B.S., MARONE G. Human skin mast cells express functional beta 1 integrins that mediate adhesion to extracellular matrix proteins. J. Immunol. 1995;154:6058–6064. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

