Regulation of 5-HT(1A) receptor-stimulated [35S]-GtpgammaS binding as measured by quantitative autoradiography following chronic agonist administration
- PMID: 11159711
- PMCID: PMC1572590
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703855
Regulation of 5-HT(1A) receptor-stimulated [35S]-GtpgammaS binding as measured by quantitative autoradiography following chronic agonist administration
Abstract
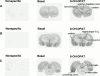
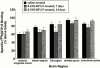
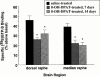
1. Because changes 5-HT(1A) receptor number do not occur following repeated agonist treatment, we hypothesized that the basis for 5-HT(1A) receptor desensitization involves changes in receptor-G protein coupling. We measured the effect of repeated agonist administration on 5-HT(1A) receptor-stimulated [(35)S]-GTPgammaS binding in forebrain areas, (i.e. anterior cingulate cortex, lateral septum, hippocampus, entorhinal cortex), and serotonergic cell body areas, the dorsal and median raphe nuclei. 2. Following treatment of rats with (+/-)8-OH-DPAT (1 mg kg(-1), s.c.) for 7 or 14 days, 5-HT(1A) receptor-stimulated [(35)S]-GTPgammaS binding was significantly attenuated in both the dorsal and median raphe nuclei. 3. 5-HT(1A) receptor-stimulated [(35)S]-GTPgammaS binding was significantly attenuated in the CA(1) region of the hippocampus after 7, but not 14 days of 8-OH-DPAT administration. 5-HT(1A) receptor-stimulated [(35)S]-GTPgammaS binding was not altered in other forebrain areas examined. 4. The binding of [(3)H]-MPPF to 5-HT(1A) receptor sites was not altered in any brain region examined following repeated agonist administration, suggesting that the observed changes in (+/-)8-OH-DPAT-stimulated [(35)S]-GTPgammaS binding were not due to changes in 5-HT(1A) receptor number. 5. Our data indicate that in serotonergic cell body areas the regulation of presynaptic 5-HT(1A) receptor function following repeated agonist administration occurs at the level of receptor-G protein interaction. In forebrain areas, however, the regulation of postsynaptic 5-HT(1A) receptor sensitivity appears not to be at the level of receptor-G protein coupling.
Figures
Similar articles
-
5-Hydroxytryptamine(1A) receptor-stimulated [(35)S]GTPgammaS binding in rat brain: absence of regional differences in coupling efficiency.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000 Feb;292(2):684-91. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000. PMID: 10640306
-
Aging alters in a region-specific manner serotonin transporter sites and 5-HT(1A) receptor-G protein interactions in hamster brain.Neuropharmacology. 2002 Jul;43(1):36-44. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(02)00072-2. Neuropharmacology. 2002. PMID: 12213257
-
Selective heterologous regulation of 5-HT1A receptor-stimulated 35S GTPgammaS binding in the anterior cingulate cortex as a result of 5-HT2 receptor activation.Brain Res. 2002 Dec 6;957(1):174-82. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)03637-5. Brain Res. 2002. PMID: 12443993
-
Autoradiography of serotonin 5-HT1A receptor-activated G proteins in guinea pig brain sections by agonist-stimulated [35S]GTPgammaS binding.J Neurochem. 1998 Mar;70(3):1258-68. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.70031258.x. J Neurochem. 1998. PMID: 9489749
-
Selective breeding of 5-HT(1A) receptor-mediated responses: application to emotion and receptor action.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2000 Dec;67(4):701-8. doi: 10.1016/s0091-3057(00)00415-9. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2000. PMID: 11166060 Review.
Cited by
-
Prolonged treatment with ligands affects ligand binding to the human serotonin(1A) receptor in Chinese hamster ovary cells.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2006 May;26(3):247-57. doi: 10.1007/s10571-006-9002-7. Epub 2006 Apr 21. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 16767512 Free PMC article.
-
Plasticity of presynaptic and postsynaptic serotonin 1A receptors in an animal model of epilepsy-associated depression.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011 May;36(6):1305-16. doi: 10.1038/npp.2011.18. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21346733 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-1β causes fluoxetine resistance in an animal model of epilepsy-associated depression.Neurotherapeutics. 2012 Apr;9(2):477-85. doi: 10.1007/s13311-012-0110-4. Neurotherapeutics. 2012. PMID: 22427156 Free PMC article.
-
Contractile effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-carboxamidotryptamine in the equine jejunum.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Jan;147(1):23-35. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706431. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16230998 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal serotonin-1A receptor function in a mouse model of anxiety induced by long-term voluntary wheel running.Synapse. 2013 Oct;67(10):648-55. doi: 10.1002/syn.21666. Epub 2013 Apr 18. Synapse. 2013. PMID: 23505009 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AGHAJANIAN G.K., SPROUSE J.S., SHELDON P., RASMUSSEN K. Electrophysiology of the central serotonin system: receptor subtypes and transducer mechanisms. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1990;600:93–103. - PubMed
-
- ANDRADE R., NICOLL R.A. Novel anxiolytics discriminate between postsynaptic serotonin receptors mediating different physiological responses on single neurons of the rat hippocampus. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1987;336:5–10. - PubMed
-
- ANDRADE R., MALENKA R.C., NICOLL R.A. A G protein couples serotonin and GABAB receptors to the same channels in hippocampus. Science. 1986;234:1261–1265. - PubMed
-
- ARTIGAS F., ROMERO L., DE MONTIGNY C., BLIER P. Acceleration of the effect of selected antidepressant drugs in major depression by 5-HT1A antagonists. Trends Neurosci. 1996;19:378–383. - PubMed
-
- BLIER P., BERGERON R. The use of pindolol to potentiate antidepressant medication. J. Clin. Psychiatry. 1998;59:16–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

